|
英文药名:ERIVEDGE(vismodegib capsule)
中文药名:维莫德吉胶囊
生产厂家:罗氏基因泰克 Continue reading
药品介绍
商品名:Erivedge
通用名:vismodegib
Erivedge(vismodegib)是一种具有选择性Hedgehog信号通路的新型口服类药物。由罗氏(Roche)的基因技术公司(Genentech)生产,已经由FDA批准用于治疗基底细胞癌,这是有史以来第一个被批准治疗基底细胞癌的药物。
Erivedge经由优先审查程序获准,是FDA批准的首个治疗转移性基底细胞癌的药物。它通过抑制Hedgehog通路起效,这种通路在大多数基底细胞癌中活跃,但仅在少许正常组织中(如毛囊)活跃。
FDA药物评价与研究中心血液肿瘤学产品部办公室主任理查德·帕兹杜尔说:“我们对涉及肿瘤的信号通路(如Hedgehog通路)的理解,使研发治疗特殊疾病的靶向药物成为可能,这种方法变得越来越普通,并有可能使抗肿瘤药物研发更快。这对可获得更有效、副作用少的治疗的患者很重要。
一项多中心临床试验评估了Erivedge的安全性和有效性,试验共纳入96例有局部晚期或转移性皮肤基底细胞癌的患者。主要终点是客观有效率(ORR),或治疗后肿瘤完全和部分缩小或癌性损害完全消失的患者百分率。在接受Erivedge治疗的转移性基底细胞癌患者中,部分缓解率为30%;在局部晚期基底细胞癌患者中,完全加部分缓解率为43%
在接受Erivedge治疗患者中观察到的最常见副作用包括肌肉痉挛、脱发,体重减轻、乏力、恶心、呕吐,味觉变化或丧失,食欲下降,便秘和腹泻。
Erivedge同其加框警告一起获准,提醒患者和医务人员该药有影响胎儿出生和致死的潜在危险。女性在接受Erivedge治疗前应确认是否妊娠。男女患者均应被警告这些风险并需要采取节育措施。
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERIVEDGE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERIVEDGE.
ERIVEDGE ® (vismodegib) capsule for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
ERIVEDGE can cause embryo-fetal death or severe birth defects when administered to a pregnant woman. ERIVEDGE is embryotoxic, fetotoxic, and teratogenic in animals. Teratogenic effects included severe midline defects, missing digits, and other irreversible malformations.
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential within 7 days prior to initiating ERIVEDGE therapy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and after ERIVEDGE therapy. Advise males of the potential risk of ERIVEDGE exposure through semen and to use condoms with a pregnant partner or a female partner of reproductive potential. Advise pregnant women of the potential risks to a fetus. (5.1, 5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ERIVEDGE® (vismodegib) capsule is a hedgehog pathway inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic basal cell carcinoma, or with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma that has recurred following surgery or who are not candidates for surgery, and who are not candidates for radiation. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose is 150 mg orally once daily. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
150 mg capsules. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Blood donation: Advise patients not to donate blood or blood products while receiving ERIVEDGE and for 7 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE. (5.2)
Semen donation: Advise males not to donate semen during and for 3 months after therapy (5.3, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence of ≥ 10%) are muscle spasms, alopecia, dysgeusia, weight loss, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, constipation, arthralgias, vomiting, and ageusia.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech, Inc. at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2)
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: May cause amenorrhea in females. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2015
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ERIVEDGE capsule is indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic basal cell carcinoma, or with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma that has recurred following surgery or who are not candidates for surgery, and who are not candidates for radiation.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose of ERIVEDGE is 150 mg taken orally once daily until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14)].
ERIVEDGE may be taken with or without food. Swallow capsules whole. Do not open or crush capsules.
If a dose of ERIVEDGE is missed, do not make up that dose; resume dosing with the next scheduled dose.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ERIVEDGE (vismodegib) capsules, 150 mg. The capsule has a pink opaque body and a grey opaque cap, with "150 mg" printed on the capsule body and "VISMO" printed on the capsule cap in black ink.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, ERIVEDGE can cause embryo-fetal death or severe birth defects when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, vismodegib was embryotoxic, fetotoxic, and teratogenic at maternal exposures lower than the human exposures at the recommended dose of 150 mg/day.
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential within 7 days prior to initiating ERIVEDGE therapy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during therapy with ERIVEDGE and for 7 months after the final dose. Advise male patients to use condoms, even after a vasectomy, to avoid potential drug exposure in pregnant partners and female partners of reproductive potential during therapy and for 3 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
5.2 Blood Donation
Advise patients not to donate blood or blood products while receiving ERIVEDGE and for 7 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE.
5.3 Semen Donation
Vismodegib is present in semen. It is not known if the amount of vismodegib in semen can cause embryo-fetal harm. Advise male patients not to donate semen during and for 3 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
ERIVEDGE capsule was administered as monotherapy at doses ≥ 150 mg orally daily in four open-label, uncontrolled, dose-ranging or fixed single dose clinical trials enrolling a total of 138 patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC). The median age of these patients was 61 years (range 21 to 101), 100% were White (including Hispanics), and 64% were male. The median duration of treatment was approximately 10 months (305 days; range 0.7 to 36 months); 111 patients received ERIVEDGE for 6 months or longer.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) were muscle spasms, alopecia, dysgeusia, weight loss, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, constipation, arthralgias, vomiting, and ageusia (Table 1).
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 10% of Advanced BCC Patients
| MedDRA Preferred Term* |
All aBCC† Patients (N = 138) |
| All Grades‡ (%) |
Grade 3 (%) |
Grade 4 (%) |
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders |
|
|
|
| Nausea |
42 (30.4%) |
1 (0.7%) |
- |
| Diarrhea |
40 (29.0%) |
1 (0.7%) |
- |
| Constipation |
29 (21.0%) |
- |
- |
| Vomiting |
19 (13.8%) |
- |
- |
| General disorders and administration site conditions |
|
|
|
| Fatigue |
55 (39.9%) |
7 (5.1%) |
1 (0.7%) |
| Investigations |
|
|
|
| Weight loss |
62 (44.9%) |
10 (7.2%) |
- |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders |
|
|
|
| Decreased appetite |
35 (25.4%) |
3 (2.2%) |
- |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
|
|
|
| Muscle spasms |
99 (71.7%) |
5 (3.6%) |
- |
| Arthralgias |
22 (15.9%) |
1 (0.7%) |
|
| Nervous system disorders |
|
|
|
| Dysgeusia |
76 (55.1%) |
- |
- |
| Ageusia |
15 (10.9%) |
- |
- |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
|
|
|
| Alopecia |
88 (63.8%) |
- |
- | MedDRA = Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities.
aBCC = Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma.
Grading according to NCI-CTCAE v3.0
Amenorrhea:
In clinical trials, a total of 3 of 10 pre-menopausal women developed amenorrhea while receiving ERIVEDGE [see Non-Clinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Laboratory Abnormalities:
Treatment-emergent Grade 3 laboratory abnormalities observed in clinical trials were hyponatremia in 6 patients (4%), hypokalemia in 2 patients (1%), and azotemia in 3 patients (2%).
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interactions are not expected between vismodegib and a substrate, inducer or inhibitor of cytochrome 450 enzymes or an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or between vismodegib and gastric pH elevating agents [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action and animal reproduction studies, ERIVEDGE can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of vismodegib during organogenesis at doses below the recommended human dose resulted in embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats [see Data]. There are no human data on the use of ERIVEDGE in pregnant women. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Report pregnancies to Genentech at 1-888-835-2555.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study, pregnant rats were administered vismodegib orally at doses of 10, 60, or 300 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Pre- and post-implantation loss were increased at doses of ≥ 60 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥ 2 times the systemic exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended human dose), which included early resorption of 100% of the fetuses. A dose of 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the AUC in patients at the recommended dose) resulted in malformations (including missing and/or fused digits, open perineum and craniofacial anomalies) and retardations or variations (including dilated renal pelvis, dilated ureter, and incompletely or unossified sternal elements, centra of vertebrae, or proximal phalanges and claws).
8.2 Lactation
No data are available regarding the presence of vismodegib in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from ERIVEDGE, advise a nursing woman that breastfeeding is not recommended during therapy with ERIVEDGE and for 7 months after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential within 7 days prior to initiating ERIVEDGE therapy.
Contraception
Females
Based on its mechanism of action and animal data, ERIVEDGE can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during therapy and for 7 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE.
Males
Vismodegib is present in semen [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. It is not known if the amount of vismodegib in semen can cause embryo-fetal harm. Advise male patients to use condoms, even after a vasectomy, to avoid drug exposure to pregnant partners and female partners of reproductive potential during therapy with and for 3 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE. Advise males of the potential risk to an embryo or fetus if a female partner of reproductive potential is exposed to ERIVEDGE. Advise males not to donate semen during therapy with and for 3 months after the final dose of ERIVEDGE.
Infertility
Females
Amenorrhea can occur in females of reproductive potential. Reversibility of amenorrhea is unknown [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ERIVEDGE capsule have not been established in pediatric patients.
In repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats, administration of oral vismodegib resulted in toxicities in bone and teeth. Effects on bone consisted of closure of the epiphyseal growth plate when oral vismodegib was administered for 26 weeks at ≥ 50 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥ 0.4 times the systemic exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended human dose). Abnormalities in growing incisor teeth (including degeneration/necrosis of odontoblasts, formation of fluid-filled cysts in the dental pulp, ossification of the root canal, and hemorrhage resulting in breakage or loss of teeth) were observed after administration of oral vismodegib at ≥ 15 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥ 0.2 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ERIVEDGE capsule did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no information on overdosage in humans. In clinical trials, ERIVEDGE capsule was administered at 540 mg orally once daily; exposure did not increase between 150 mg and 540 mg daily.
11 DESCRIPTION
Vismodegib is an inhibitor of the hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, which is described chemically as 2-Chloro-N-(4-chloro-3-(pyridin-2-yl)phenyl)-4-(methylsulfonyl)benzamide. The molecular formula is C19H14Cl2N2O3S. The molecular weight is 421.30 g/mol and the structural formula is:
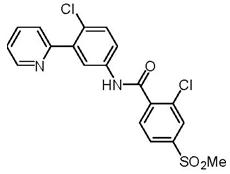
Vismodegib is a crystalline free base with a pKa (pyridinium cation) of 3.8, appearing as a white to tan powder. The solubility of vismodegib is pH dependent with 0.1 μg/mL at pH 7 and 0.99 mg/mL at pH 1. The partition coefficient (log P) is 2.7.
Each ERIVEDGE (vismodegib) capsule for oral administration contains 150 mg vismodegib and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, sodium lauryl sulfate, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, talc, and magnesium stearate (non-bovine). The capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide, and black iron oxide. The black printing ink contains shellac and black iron oxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Vismodegib is an inhibitor of the Hedgehog pathway. Vismodegib binds to and inhibits Smoothened, a transmembrane protein involved in Hedgehog signal transduction.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The QTc interval was not affected by therapeutic doses of ERIVEDGE in a thorough QTc trial.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The single dose absolute bioavailability of vismodegib is 31.8%. Absorption is saturable as evidenced by the lack of dose proportional increase in exposure after a single dose of 270 mg or 540 mg vismodegib. ERIVEDGE capsule may be taken without regard to meals because the systemic exposure of vismodegib at steady state is not affected by food.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of vismodegib ranges from 16.4 to 26.6 L. Vismodegib plasma protein binding in patients is greater than 99%. Vismodegib binds to both human serum albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) and binding to AAG is saturable.
In a pharmacokinetic study, male patients (n=3) had an average concentration of vismodegib in semen on day 8 that was 6.5% of the average steady state concentration (Css) observed in plasma.
Metabolism
Greater than 98% of the total circulating drug-related components are the parent drug. Metabolic pathways of vismodegib in humans include oxidation, glucuronidation, and pyridine ring cleavage. The two most abundant oxidative metabolites recovered in feces are produced in vitro by recombinant CYP2C9 and CYP3A4/5.
Elimination
Vismodegib and its metabolites are eliminated primarily by the hepatic route with 82% of the administered dose recovered in the feces and 4.4% recovered in urine. The estimated elimination half-life (t1/2) of vismodegib is 4 days after continuous once-daily dosing and 12 days after a single dose.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment: In a dedicated clinical study, the mean systemic exposure (AUC 0-24hr) of vismodegib was increased by 24% in patients with mild (n=8), 31% in patients with moderate (n=6) and decreased 14% in patients with severe (n=3) hepatic impairment when compared to patients with normal hepatic function (n=9) after 8 days of daily ERIVEDGE administration. The NCI Organ Dysfunction Working Group criteria for hepatic impairment were used in the study. Mild hepatic impairment was defined as normal total bilirubin and aspartate transaminase (AST) > upper limit of normal (ULN) or total bilirubin > 1.0 to 1.5 times ULN, moderate hepatic impairment as total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3.0 times ULN, and severe hepatic impairment as total bilirubin > 3.0 to 10.0 times ULN.
Renal Impairment: Renal excretion of vismodegib after oral administration of ERIVEDGE is low (<5%). The population pharmacokinetic analysis suggested no clinically relevant effect of renal impairment on the systemic exposure of vismodegib, based on pharmacokinetic data from patients with mild (CLcr 50 to 79 mL/min, n=58), and moderate (CLcr 30 to 49 mL/min, n=16) renal impairment.
Weight, Age, and Sex: The results of a population pharmacokinetic analysis suggested no clinically relevant effect of weight (range: 41-140 kg), age (range: 26-89 years), and sex on the systemic exposure of vismodegib.
Drug Interaction Studies
Effect of Drugs on Vismodegib: Coadministration of ERIVEDGE with fluconazole (a moderate CYP2C9 inhibitor and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased mean AUC0-24hr and steady-state concentrations of vismodegib by 1.3-fold in healthy subjects. A strong inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp (itraconazole) or a proton pump inhibitor (rabeprazole) had no effect on the steady-state systemic exposure of vismodegib when coadministered with ERIVEDGE in healthy subjects.
Effects of Vismodegib on Other Drugs: Results of a drug interaction study conducted in cancer patients demonstrated that the systemic exposure of rosiglitazone (a CYP2C8 substrate) or oral contraceptives (ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone) is not altered when either drug is coadministered with vismodegib.
In vitro studies suggest that vismodegib is an inhibitor of CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and the transporter BCRP and that vismodegib is not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with vismodegib have not been conducted. Pilomatricoma (a benign cutaneous neoplasm) was observed in rats administered oral vismodegib for 26 weeks at 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8 times the systemic exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended human dose).
Vismodegib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in the in vitro human chromosomal aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes or in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Studies to assess the potential of vismodegib to affect fertility have not been conducted; however, data from repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats and dogs indicate that male and female reproductive function and fertility may be impaired in patients receiving ERIVEDGE capsule. In a 26-week toxicology study in rats, a relative decrease in percent motile sperm was observed at ≥ 15 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥ 0.3 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose). In dogs, increased numbers of degenerating germ cells and hypospermia were observed in young animals administered oral vismodegib for 4 weeks at ≥ 50 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥ 2 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose). No corresponding findings were observed in sexually mature dogs at similar doses in 13-week and 26-week toxicology studies. A decrease in the number of corpora lutea was observed in female rats administered oral vismodegib for 26 weeks at 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose).
13.2 Animal Toxicology
Neurologic effects characterized as limb or body tremors or twitching were observed in rats administered oral vismodegib for 4 weeks or longer at ≥ 50 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥ 0.4 times the AUC in patients at the recommended human dose). These observations resolved upon discontinuation of dosing and were not associated with microscopic findings.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
A single, international, single-arm, multi-center, open-label, 2-cohort trial was conducted in 104 patients with either metastatic basal cell carcinoma (mBCC) (n = 33) or locally advanced BCC (laBCC) (n = 71). Patients with laBCC were required to have lesions that had recurred after radiotherapy, unless radiotherapy was contraindicated or inappropriate (e.g. Gorlin syndrome; limitations because of location of tumor or cumulative prior radiotherapy dose), and where the lesions were either unresectable or surgical resection would result in substantial deformity. Patients were to receive 150 mg vismodegib per day orally until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome measure of the trial was objective response rate (ORR) as assessed by an independent review facility (IRF). In the mBCC cohort, tumor response was assessed according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.0. In the laBCC cohort, tumor response evaluation included measurement of externally assessable tumor (including scar) and assessment for ulceration in photographs, radiographic assessment of target lesions (if appropriate), and tumor biopsy. An objective response in laBCC required at least one of the following criteria and absence of any criterion for disease progression: (1) ≥ 30% reduction in lesion size [sum of the longest diameter (SLD)] from baseline in target lesions by radiographic assessment; (2) ≥ 30% reduction in SLD from baseline in externally visible dimension of target lesions; (3) complete resolution of ulceration in all target lesions. Complete response was defined as objective response (as defined above) with no residual BCC on sampling tumor biopsy. Disease progression was defined as any of the following: (1) ≥ 20% increase in the SLD from nadir in target lesions (either by radiography or by externally visible dimension); (2) new ulceration of target lesions persisting without evidence of healing for at least 2 weeks; (3) new lesions by radiographic assessment or physical examination; (4) progression of non-target lesions by RECIST.
Of the 104 patients enrolled, 96 patients were evaluable for ORR. Twenty-one percent of patients carried a diagnosis of Gorlin syndrome. The median age of the efficacy evaluable population was 62 years (46% were at least 65 years old), 61% male and 100% White. For the mBCC cohort (n = 33), 97% of patients had prior therapy including surgery (97%), radiotherapy (58%), and systemic therapies (30%). For the laBCC cohort (n = 63), 94% of patients had prior therapies including surgery (89%), radiotherapy (27%), and systemic/topical therapies (11%). The median duration of treatment was 10.2 months (range 0.7 to 18.7 months).
The key outcome measures are presented in Table 2, below.
Table 2: Objective Response Rate: Efficacy-Evaluable Patients*
mBCC
(n = 33) |
laBCC
(n = 63) |
|
| IRF†-Confirmed ORR, n (%) |
10 (30.3) |
27 (42.9) |
| (95% CI) |
(15.6, 48.2) |
(30.5, 56.0) |
| Complete response‡ |
0 (0.0) |
13 (20.6) |
| Partial response |
10 (30.3) |
14 (22.2) |
| Median Response Duration (months) |
7.6 |
7.6 |
| (95% CI§) |
(5.6, NE) |
(5.7, 9.7) | Patients who received at least one dose of ERIVEDGE with independent pathologist-confirmed diagnosis of BCC
IRF = Independent Review Facility
For laBCC, complete response was defined as objective response with no residual BCC on sampling tumor biopsy.
CI = Confidence Interval
NE = Not estimable
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each ERIVEDGE (vismodegib) capsule has a pink opaque body and a grey opaque cap with "150 mg" printed on the capsule body and "VISMO" printed on the capsule cap in black ink. ERIVEDGE capsules are available in bottles of 28 capsules (NDC 50242-140-01).
Store at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=eb368bb6-80e3-4df9-8a85-91df0a2ada6a
美国包装
欧洲包装
 
罗氏基底细胞癌药物Erivedge获欧盟有条件批准
2013年7月15日,罗氏(Roche)今日宣布,欧盟委员会(EC)已授予Erivedge(vismodegib)有条件批准(conditional approval),用于不适宜手术或放疗治疗的有症状转移性基底细胞癌(BCC)或局部晚期BCC成人患者的治疗。该项批准,使Erivedge成为欧盟首个获批用于这一严重危机生命的皮肤癌的药物。
有条件批准授予具有积极效益/风险评估的产品,以满足一种严重未获满足的医疗需求,将带来重大的公共卫生利益。根据有条件批准的规定,罗氏将提供目前正在开展的全球安全性研究中有关Erivedge治疗晚期BCC的额外数据。
2012年1月,FDA通过优先审查程序批准了Erivedge,成为美国首个获批用于晚期BCC治疗的药物,专门用于已经不能开刀或化疗治疗的局部晚期基底细胞癌或癌变已扩散至身体其他器官的BCC患者的治疗。自2012年10月,Erivedge已获瑞士、澳大利亚、以色列、韩国、墨西哥、厄瓜多尔批准。目前,罗氏正积极与多国的监管机构密切合作,确保Erivedge能尽快上市。
基底细胞癌是最常见的皮肤癌之一,它源于皮肤表层,患者同时不会感到疼痛。对于经常暴露在阳光下或是紫外线照射的皮肤病发的几率最大。
Erivedge是一种日服的药片,通过抑制Hedgehog 路径来发挥作用,这种路径在大多数基底细胞癌中活性很高。
|





