|
2013年4月30日,美国食品药品管理局(FDA)已批准扩大紧急避孕药Plan B One-Step(左炔诺孕酮,1.5 mg)作为非处方药(OTC)的适用人群范围。
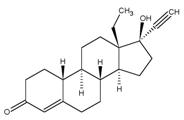
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Plan B (2 doses of 0.75 mg levonorgestrel taken 12 hours apart). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Gastrointestinal Disorders Abdominal Pain, Nausea, Vomiting General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue Nervous System Disorders Dizziness, Headache Reproductive System and Breast Disorders Dysmenorrhea, Irregular Menstruation, Oligomenorrhea, Pelvic Pain 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS Drugs or herbal products that induce enzymes, including CYP3A4, that metabolize progestins may decrease the plasma concentrations of progestins, and may decrease the effectiveness of progestin-only pills. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of progestin-only pills include: barbiturates bosentan carbamazepine felbamate griseofulvin oxcarbazepine phenytoin rifampin St. John’s wort topiramate Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma levels of the progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration with HIV protease inhibitors or with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Consult the labeling of all concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with progestin-only pills or the potential for enzyme alterations. 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy Many studies have found no harmful effects on fetal development associated with long-term use of contraceptive doses of oral progestins. The few studies of infant growth and development that have been conducted with progestin-only pills have not demonstrated significant adverse effects. 8.3 Nursing Mothers In general, no adverse effects of progestin-only pills have been found on breastfeeding performance or on the health, growth, or development of the infant. However, isolated post-marketing cases of decreased milk production have been reported. Small amounts of progestins pass into the breast milk of nursing mothers taking progestin-only pills for long-term contraception, resulting in detectable steroid levels in infant plasma. 8.4 Pediatric Use Safety and efficacy of progestin-only pills for long-term contraception have been established in women of reproductive age. Safety and efficacy are expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents less than 17 years and for users 17 years and older. Use of Plan B One-Step emergency contraception before menarche is not indicated. 8.5 Geriatric Use This product is not intended for use in postmenopausal women. 8.6 Race No formal studies have eva luated the effect of race. However, clinical trials demonstrated a higher pregnancy rate in Chinese women with both Plan B and the Yuzpe regimen (another form of emergency contraception). There was a non-statistically significant increased rate of pregnancy among Chinese women in the Plan B One-Step trial. The reason for this apparent increase in the pregnancy rate with emergency contraceptives in Chinese women is unknown. 8.7 Hepatic Impairment No formal studies were conducted to eva luate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of Plan B One-Step. 8.8 Renal Impairment No formal studies were conducted to eva luate the effect of renal disease on the disposition of Plan B One-Step. 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE Levonorgestrel is not a controlled substance. There is no information about dependence associated with the use of Plan B One-Step. 10 OVERDOSAGE There are no data on overdosage of Plan B One-Step, although the common adverse event of nausea and associated vomiting may be anticipated. 11 DESCRIPTION The Plan B One-Step tablet contains 1.5 mg of a single active steroid ingredient, levonorgestrel [18,19-Dinorpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one-13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-, (17 α)-(-)-], a totally synthetic progestogen. The inactive ingredients are colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, potato starch, and talc. Levonorgestrel has a molecular weight of 312.45, and the following structural and molecular formulas: C21H28O2
Distribution The apparent volume of distribution of levonorgestrel is reported to be approximately 1.8 L/kg. It is about 97.5 to 99% protein-bound, principally to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and, to a lesser extent, serum albumin. Metabolism Following absorption, levonorgestrel is conjugated at the 17β-OH position to form sulfate conjugates and, to a lesser extent, glucuronide conjugates in plasma. Significant amounts of conjugated and unconjugated 3α, 5β-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel are also present in plasma, along with much smaller amounts of 3α, 5α-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel and 16βhydroxylevonorgestrel. Levonorgestrel and its phase I metabolites are excreted primarily as glucuronide conjugates. Metabolic clearance rates may differ among individuals by several-fold, and this may account in part for the wide variation observed in levonorgestrel concentrations among users. Excretion About 45% of levonorgestrel and its metabolites are excreted in the urine and about 32% are excreted in feces, mostly as glucuronide conjugates. Specific Populations Pediatric This product is not intended for use in the premenarcheal population, and pharmacokinetic data are not available for this population. Geriatric This product is not intended for use in postmenopausal women, and pharmacokinetic data are not available for this population. Race No formal studies have eva luated the effect of race. However, clinical trials demonstrated a higher pregnancy rate in Chinese women with both Plan B and the Yuzpe regimen (another form of emergency contraception). There was a non-statistically significant increased rate of pregnancy among Chinese women in the Plan B One-Step trial. The reason for this apparent increase in the pregnancy rate with emergency contraceptives in Chinese women is unknown [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.6)]. Hepatic Impairment No formal studies were conducted to eva luate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of Plan B One-Step. Renal Impairment No formal studies were conducted to eva luate the effect of renal disease on the disposition of Plan B One-Step. Drug-Drug Interactions No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Plan B One-Step [see DRUG INTERACTIONS (7)]. 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Carcinogenicity: There is no evidence of increased risk of cancer with short-term use of progestins. There was no increase in tumorgenicity following administration of levonorgestrel to rats for 2 years at approximately 5 µg/day, to dogs for 7 years at up to 0.125 mg/kg/day, or to rhesus monkeys for 10 years at up to 250 µg/kg/day. In another 7 year dog study, administration of levonorgestrel at 0.5 mg/kg/day did increase the number of mammary adenomas in treated dogs compared to controls. There were no malignancies. Genotoxicity: Levonorgestrel was not found to be mutagenic or genotoxic in the Ames Assay, in vitro mammalian culture assays utilizing mouse lymphoma cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells, and in an in vivo micronucleus assay in mice. Fertility: There are no irreversible effects on fertility following cessation of exposures to levonorgestrel or progestins in general. 14 CLINICAL STUDIES A double-blind, randomized, multicenter, multinational study eva luated and compared the efficacy and safety of three different regimens for emergency contraception. Subjects were enrolled at 15 sites in 10 countries; the racial/ethnic characteristics of the study population overall were 54% Chinese, 34% Caucasian, and 12% Black or Asian (other than Chinese). 2,381 healthy women with a mean age of 27 years, who needed emergency contraception within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse were involved and randomly allocated into one of the two levonorgestrel groups. A single dose of 1.5 mg of levonorgestrel (Plan B One-Step) was administered to women allocated into group 1. Two doses of 0.75 mg levonorgestrel 12 hours apart (Plan B) were administered to women in group 2. In the Plan B One-Step group, 16 pregnancies occurred in 1,198 women and in the Plan B group, 20 pregnancies occurred in 1,183 women. The number of pregnancies expected in each group was calculated based on the timing of intercourse with regard to each woman’s menstrual cycle. Among women receiving Plan B One-Step, 84% of expected pregnancies were prevented and among those women taking Plan B, 79% of expected pregnancies were prevented. The expected pregnancy rate of 8% (with no contraceptive use) was reduced to approximately 1% with Plan B One-Step. Emergency contraceptives are not as effective as routine contraception since their failure rate, while low based on a single use, would accumulate over time with repeated use [see INDICATIONS AND USAGE (1)]. In the clinical study, bleeding disturbances were the most common adverse event reported after taking the levonorgestrel-containing regimens. More than half of the women had menses within two days of the expected time; however, 31% of women experienced change in their bleeding pattern during the study period; 4.5% of women had menses more than 7 days after the expected time. 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING The Plan B One-Step (levonorgestrel) tablet 1.5 mg is available in a PVC/aluminum foil blister package. The tablet is almost white, round, and marked G00 on one side. NDC 51285-942-88 (1 tablet unit of use package) Store Plan B One-Step at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Plan B One-Step(levonorgestrel) tablet简介:
2013年4月30日,美国食品药品管理局(FDA)已批准扩大紧急避孕药Plan B One-Step(左炔诺孕酮,1.5 mg)作为非处方药(OTC)的适用人群范围。Plan B One-Step是已知紧急避孕药意向在非保护性交或已知或怀疑避 ... 责任编辑:admin
|
最新文章更多推荐文章更多热点文章更多 |