|
英文药名:ELOCTATE(AntihemophilicFactor[Recombinant],Fc Fusion Protein) 中文药名:抗血友病因子(重组),Fc融合蛋白]注射冻干粉 生产厂家:百健艾迪公司
A guide for dosing ELOCTATE during surgery (perioperative management) is provided in Table 2. Consideration should be given to maintaining a Factor VIII activity at or above the target range. Table 2: Dosing for Perioperative Management
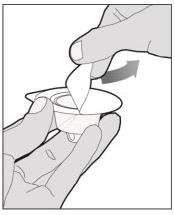
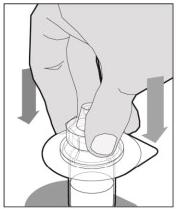
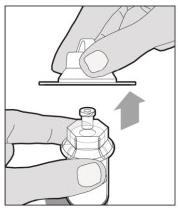
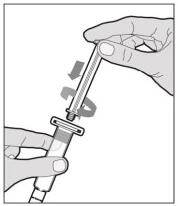
The recommended starting regimen is 50 IU/kg of ELOCTATE administered every 4 days. Adjust the regimen based on patient response with dosing in the range of 25-65 IU/kg at 3-5 day intervals. For children <6 years of age, the recommended starting regimen is 50 IU/kg of ELOCTATE administered twice weekly. Adjust the regimen based on patient response with dosing in the range of 25-65 IU/kg at 3-5 day intervals. More frequent or higher doses up to 80 IU/kg may be required. [see Use In Specific Populations (8.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] 2.2 Preparation and Reconstitution 1.Use aseptic technique (clean and germ free) and a flat work surface during the reconstitution procedure. 2.Allow the vial of ELOCTATE and pre-filled diluent syringe to reach room temperature before use. 3.Remove the plastic cap from the vial and wipe the rubber stopper of the vial with an alcohol wipe. Allow the rubber stopper to dry. 4.Completely remove the backing from the vial adapter package by peeling back the lid. Do not remove the vial adapter from the package or touch the inside of the package of the adapter.
Clinical trial subjects were monitored for neutralizing antibodies to Factor VIII. No subjects developed confirmed neutralizing antibodies to Factor VIII. One 25 year old subject had a transient, positive, neutralizing antibody of 0.73 BU at week 14, which was not confirmed upon repeat testing 18 days later and thereafter. The detection of antibodies that are reactive to Factor VIII is highly dependent on many factors, including the sensitivity and specificity of the assay, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications and underlying disease. Therefore, it may be misleading to compare of the incidence of antibodies to ELOCTATE with the incidence of antibodies to other products. 6.2 Postmarketing Experience The following adverse reaction has been identified during the post-approval use of ELOCTATE. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Factor VIII inhibitor development 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy Risk Summary There are no studies of ELOCTATE use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the indicated population is unknown; however, the background risk of major birth defects in the U.S. general population is 2-4% and of miscarriage is 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies. Animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies have not been conducted with ELOCTATE. In a placental transfer study, ELOCTATE was detected in murine fetal blood samples at approximately 1% of the maternal blood levels (range, 0.2% to 1.9%), 3 to 4 hours following dosing of pregnant mice with 260 to 650 times the clinical dose of 20 to 50 IU/kg ELOCTATE [see Data]. It is not known whether ELOCTATE can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman, or whether it can affect reproduction capacity. If ELOCTATE is clearly needed to treat a pregnant woman, advise the patient that the risks to the mother and to the fetus are unknown. Data Animal Data Pregnant, genetically-modified, FVIII-deficient mice (Hem A mice) were injected intravenously with a single dose of 400 IU (approximately 13,000 IU/kg) ELOCTATE at the end of pregnancy on Gestation Day 19. Blood samples were collected from the maternal mice and the fetuses 3 to 4 hours after dosing, and FVIII activity was measured in both maternal and fetal plasma using a FVIII chromogenic assay. After dosing pregnant HemA mice with ELOCTATE, FVIII activity in fetal blood was approximately 1% of the maternal blood levels, suggesting that placental transfer of ELOCTATE may occur. The relevance of these data to humans is unknown. 8.2 Lactation Risk Summary There is no information regarding the presence of ELOCTATE in human milk, its effects on the breastfed infant, or its effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ELOCTATE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ELOCTATE or from the underlying maternal condition. 8.4 Pediatric Use Safety and efficacy studies have been performed in 82 previously treated, pediatric patients <18 years of age who received at least one dose of ELOCTATE as part of routine prophylaxis, on-demand treatment of bleeding episodes, or perioperative management. Adolescent subjects were enrolled in the adult and adolescent safety and efficacy trial, and subjects <12 were enrolled in a pediatric trial. Pharmacokinetic data from a pediatric study of the 54 evaluable subjects <12 years of age showed that no dose adjustment was required for patients ≥6 years old. Children age 1 to 5 years had a shorter half-life and higher clearance (adjusted for body weight); therefore, a higher dose or more frequent dosing may be needed in this age group. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] 8.5 Geriatric Use Clinical studies of ELOCTATE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether or not they respond differently from younger subjects. 11 DESCRIPTION ELOCTATE, Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein, is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, lyophilized powder for reconstitution for intravenous injection. The product is supplied in single use vials containing nominal potencies of 250, 500, 750, 1000, 1500, 2000 or 3000 international units (IU). Each vial of ELOCTATE is labeled with the actual content in IU. The powder for injection is reconstituted with 3 mL sterile water for injection (SWFI) supplied in a sterile prefilled syringe. The reconstituted product contains the excipients: sucrose, sodium chloride, L-histidine, calcium chloride and polysorbate 20. ELOCTATE contains no preservatives. B-domain deleted recombinant Factor VIII, Fc fusion protein (BDD-rFVIIIFc) is the active ingredient in ELOCTATE. BDD-rFVIIIFc is a recombinant protein consisting of a B-domain deleted analogue of human Coagulation Factor VIII covalently linked to the human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) Fc domain sequence. The Factor VIII portion of the molecule has a 90 kDa heavy chain and an 80 kDa light chain (similar to endogenous Factor VIII), which are linked by 14 (of 908) amino acids from the central B-domain. The FVIII portion has post-translational modifications comparable to endogenous Factor VIII. The Fc domain of the molecule contains the hinge, CH2, and CH3 regions of IgG1. BDD-rFVIIIFc contains 1890 amino acids with an apparent molecular weight of 220 kDa. The majority of the expressed protein is proteolytically processed to a two chain molecule; however ELOCTATE may also contain up to 39% of a single chain, non-processed form. Both molecules have been shown to have comparable Factor VIII activity. BDD-rFVIIIFc is produced by recombinant DNA technology from a human embryonic kidney (HEK) cell line, which has been extensively characterized. The HEK cell line expresses BDD-rFVIIIFc into a defined, cell culture medium that does not contain any proteins derived from animal or human sources. BDD-rFVIIIFc is purified using a series of chromatography steps, including affinity capture with a recombinant, single chain antibody fragment produced in a yeast expression system. No human or animal derived proteins are used in the purification or formulation processes. The production process also incorporates two dedicated viral clearance steps - a detergent treatment step for inactivation and a 15 nm filtration step for removal of viruses. 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action ELOCTATE is a recombinant fusion protein that temporarily replaces the missing Coagulation Factor VIII needed for effective hemostasis. ELOCTATE contains the Fc region of human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1), which binds to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). FcRn is part of a naturally occurring pathway that delays lysosomal degradation of immunoglobulins by cycling them back into circulation and prolonging their plasma half-life. 12.2 Pharmacodynamics Hemophilia A is a bleeding disorder characterized by a deficiency of functional coagulation Factor VIII, resulting in a prolonged, patient plasma clotting time as measured by the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) assay. Treatment with ELOCTATE normalizes the aPTT over the effective dosing period. 12.3 Pharmacokinetics The pharmacokinetics (PK) of ELOCTATE (rFVIIIFc) were evaluated in 28 subjects following a 10 minute intravenous infusion of a single dose of 50 IU/kg. The PK parameters were based on plasma FVIII activity measured by the one-stage clotting assay. The PK profile obtained at week 14, after repeated dosing, was comparable with the PK profile obtained after the first dose. The PK data demonstrate that ELOCTATE has a prolonged circulating half-life. Time to 1% was 5.10 days (95% CI: 4.54, 5.66). The terminal plasma half-life of ELOCTATE when compared against a currently marketed recombinant Factor VIII (ADVATE?) was 1.5 fold longer. Pediatric and Adolescent Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters of ELOCTATE were determined for adolescents (ages 12 to 17 years) in the adult and adolescent study and for children (ages 1 to 5 years and 6 to 11 years) in the pediatric study. Table 4 presents the PK parameters calculated from the pediatric data of 65 subjects, less than 18 years of age, after receiving a single 50 IU/kg dose. Compared to adults and adolescents, body weight adjusted clearance was 75% higher in children 1 to 5 years of age. These results indicate a need for dose adjustments in children 1 to 5 years of age. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] The PK evaluation of pediatric subjects, ages 6 to 17 years, showed that their PK profiles and arithmetic means of PK parameters are similar to those of adults. Therefore, for subjects 6 years and older, an age-based dose adjustment is not required. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] Table 4: Comparison of PK Parameters of ELOCTATE by Age
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Long-term animal studies investigating the carcinogenic effects of ELOCTATE have not been conducted. In vitro and in vivo testing of ELOCTATE for mutagenicity or effects on fertility was not performed. 14 CLINICAL STUDIES The safety and efficacy of ELOCTATE was evaluated in two multi-center, prospective, open-label clinical trials (adult and adolescent study and pediatric study), and is being evaluated in an ongoing extension study. The adult and adolescent study compared the efficacy of each of two prophylactic treatment regimens (individualized and fixed weekly) to episodic (on-demand) treatment; determined hemostatic efficacy in the treatment of bleeding episodes; and determined hemostatic efficacy during perioperative management in subjects undergoing major surgical procedures. The study enrolled a total of 165 previously treated male patients (PTPs) with severe Hemophilia A (<1% endogenous Factor VIII activity or a genetic mutation consistent with severe Hemophilia A). Subjects were aged 12 to 65 years, including 13 pediatric subjects aged 12 to 17 years. Of the 165 enrolled subjects, 164 received at least one dose of ELOCTATE and 163 (98%) were evaluable for efficacy. A total of 153 subjects (93%) completed the study. The pediatric study evaluated the efficacy of individualized prophylactic treatment; determined hemostatic efficacy in the treatment of bleeding episodes; and determined hemostatic efficacy during perioperative management in subjects undergoing surgical procedures. The study enrolled a total of 71 previously treated male pediatric patients with severe hemophilia A (<1% endogenous FVIII activity or a genetic mutation consistent with severe hemophilia A). Of the 71 enrolled subjects, 69 received at least 1 dose of ELOCTATE and were evaluable for efficacy. All subjects were less than 12 years of age (35 were 1 to 5 years of age and 34 were 6 to 11 years of age). The extension study is an ongoing extension study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of prophylactic treatment regimens or on-demand treatment; as well as hemostatic efficacy during perioperative management in subjects undergoing surgical procedures. The study has enrolled a total of 211 previously treated male patients (aged 2 to 66 years old) with severe hemophilia A who completed the adult and adolescent study or the pediatric study. On-demand Treatment and Control of Bleeding Episodes In the adult and adolescent study, a total of 757 bleeding episodes in 106 subjects were treated with ELOCTATE. The majority of the bleeding episodes were spontaneous and localized in joints. The median dose per injection used to treat a bleeding episode was 27.35 (IQR 22.73, 32.71) IU/kg. Assessment of response to each injection was recorded by subjects at 8-12 hours after treatment. A 4-point rating scale of excellent, good, moderate, and no response was used to assess response. Efficacy in control of bleeding episodes in subjects ≥12 years of age is summarized in Table 5. Table 5: ELOCTATE Efficacy in Control of Bleeding in Subjects ≥12 Years of Age
The hemostatic efficacy in treatment of bleeds was rated excellent or good in 92.6% for all evaluable first injections. Table 6: ELOCTATE Efficacy in Control of Bleeding in Pediatric Subjects <12 Years of Age
Major Surgeries Hemostatic efficacy was assessed in twenty-two (22) surgeries in twenty (20) subjects from the adult and adolescent study and the extension study. There were no major surgeries in the pediatric study. Most subjects (95.5%) received a single pre-operative dose to maintain hemostasis during surgery. The median dose per injection to maintain hemostasis during surgery was 57.4 IU/kg (range 45-102). On the day of surgery, most subjects received a second injection. The total dose on the day of surgery ranged from 50.8-126.6 IU/kg. Hemostatic response was assessed by the investigator using ordinal scales as follows: Excellent: Intraoperative and postoperative blood loss similar to (or less than) the nonhemophilic patient. No extra doses of rFVIIIFc needed and blood component transfusions required are similar to nonhemophilic patient Good: Intraoperative and/or postoperative bleeding slightly increased over expectations for the nonhemophilic patient, but the difference was not clinically significant. Intraoperative blood loss no more than 250 mL greater than expected for a nonhemophilic patient and no extra doses of rFVIIIFc needed and blood component transfusions required are similar to nonhemophilic patient Fair: Intraoperative and/or postoperative blood loss is increased over expectation for the nonhemophilic patient and additional treatment was needed. Intraoperative blood loss 250 to 500 mL greater than expected for person without hemophilia or extra dose of rFVIIIFc needed or increased blood component transfusion requirement Poor/none: Significant intraoperative and/or postoperative bleeding that was substantially increased over expectations for the nonhemophilic patient, required intervention, and was not explained by a surgical/medical issue other than hemophilia: Intraoperative blood loss >500 mL greater than for the nonhemophilic patient or unexpected hypotension or unexpected transfer to intensive care unit due to bleeding or substantially increased blood component transfusion requirement For twenty-two (22) major surgeries in twenty (20) subjects, hemostatic response was assessed and rated as excellent in 19 (86%) surgeries and good in 3 (14%) surgeries. Types of surgeries assessed include major orthopedic procedures such as joint replacements (bilateral knee, as well as unilateral elbow, hip and knee replacements), ankle fusion and amputation. Other major surgeries include appendectomy, arthroscopy, spinal surgery, and inguinal hernia repair. Minor Surgeries A hemostatic assessment of 32 minor surgical procedures in 29 subjects from all three studies was conducted with a 100% excellent or good response. Routine Prophylaxis Adult and Adolescent Study The efficacy of routine prophylaxis was evaluated against on-demand treatment. A total of 117 subjects received an individualized, twice weekly regimen, which started with 25 IU/kg on the first day followed by 50 IU/kg on the fourth day. The dose and interval were adjusted within the range of 25 – 65 IU/kg every 3-5 days to maintain trough levels between 1% and 3% above baseline, or higher, as clinically indicated to prevent bleeding. The median dosing interval was 3.5 days. Among the 112 subjects treated for at least 6 months, 111 (99%) achieved a dosing interval of three days or longer, 39 (35%) achieved a dosing interval of 4 days or longer, and 33 (29%) achieved a dosing interval of 5 days or longer during the last 3 months on study. Twenty-three subjects received 65 IU/kg of ELOCTATE once weekly for a median period of 28 weeks. An additional 23 subjects received episodic (on-demand) doses of ELOCTATE for the treatment of bleeding episodes and were on study for a median period of 29 weeks. Using a negative binomial model to analyze the annualized bleeding rate (ABR), there was a statistically significant reduction in ABR of 92% (p<0.001) for subjects in the individualized prophylaxis arm and a statistically significant reduction of 76% (p<0.001) for subjects in the weekly prophylaxis arm compared to the episodic (on-demand) arm. Fifty-three (53) of 117 (45%) subjects experienced no bleeding episodes while on individualized prophylaxis and 4 of 23 (17%) subjects experienced no bleeding episodes while on weekly prophylaxis. Median ABRs in subjects evaluable for efficacy is summarized in Table 7. Table 7: Median (IQR)1 Annualized Bleed Rate by ELOCTATE Treatment Arm in Subjects ≥ 12 Years of Age
Pediatric Study Sixty-nine (69) subjects received ELOCTATE on an individualized prophylactic dose regimen starting with a twice weekly regimen consisting of 25 IU/kg on the first day followed by 50 IU/kg on the fourth day. The dose could be adjusted within the range of 25-80 IU/kg with a minimum dosing interval of every 2 days to maintain trough of 1% above baseline or as clinically indicated to prevent bleeding. The median dosing interval was 3.49 days (interquartile range, 3.46 to 3.51 days) with no difference in the median dosing interval between age cohorts. 89.9% of subjects remained on a twice weekly interval. The median weekly dose of ELOCTATE for subjects 1-5 years of age was 91.63 IU/kg (interquartile range (IQR), 84.72 to 104.56 IU/kg). For subjects in the 6 to 11 years of age cohort, the median weekly dose was 86.88 IU/kg (IQR, 79.12 to 103.08 IU/kg). Of all subjects, 32 (46.4%) experienced no bleeding episodes (18 subjects (51.4%) 1-5 years of age and 14 subjects (41.2%) 6 to 11 years of age). A presentation of the median ABRs evaluable for efficacy is summarized in Table 8. Table 8: Median (IQR)1 Annualized Bleed Rate in Pediatric Subjects <12 Years of Age
1.Sommer JM, Moore N, McGuffie-Valentine B, et al. Comparative field study evaluating the activity of recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein in plasma samples at clinical haemostasis laboratories. Haemophilia. 2014;20:294 – 300. 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING How Supplied ELOCTATE is supplied in kits comprising a single use vial containing nominally, 250, 500, 750, 1000, 1500, 2000, or 3000 international units (IU) of Factor VIII potency, a pre-filled syringe with 3 mL sterile water for injection, and a sterile vial adapter (reconstitution device). The actual amount of ELOCTATE in IU is stated on the label and carton of each vial. Components used in the packaging of ELOCTATE contain no natural rubber latex.
Prior to reconstitution: Store ELOCTATE in the original package to protect the ELOCTATE vials from light. Store ELOCTATE in powder form at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze to avoid damage to the pre-filled diluent syringe. ELOCTATE may be stored at room temperature, not to exceed 30°C (86°F), for a single period of up to 6 months, within the expiration date printed on the label. If stored at room temperature, record the date that ELOCTATE is removed from refrigeration on the carton in the area provided. After storage at room temperature, do not return the product to the refrigerator. Do not use beyond the expiration date printed on the vial or 6 months after the date that was written on the carton, whichever is earlier. After Reconstitution: The reconstituted product may be stored at room temperature, not to exceed 30°C (86°F), for up to 3 hours. Protect from direct sunlight. After reconstitution, if the product is not used within 3 hours, it must be discarded. Do not use ELOCTATE if the reconstituted solution is cloudy or has particulate matter. Discard any unused ELOCTATE.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||