美国食品药品管理局(FDA)和Regeneron公司宣布Eylea(阿柏西普)已获准用于治疗新生血管性(湿性)年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)。
美国食品药品监督管理局药物评价和研究中心抗微生物产品办公室主任Edward Cox, M.D., M.P.H说:“Eylea 对成年湿性AMD是一个重要的治疗选择”“它是潜在失明疾病和新治疗选择的可供利用是重要的。”
EYLEA™ (aflibercept)注射剂或玻璃体内注射
美国初始批准:2011
制造商:
Regeneron公司
类药物:
重组融合蛋白(人类VEGF抑制剂+人IgG1)。
活性成分(S):
Aflibercept 40mg/mL; OPH玻璃体内注射soln;不含防腐剂。
指示(S):
治疗新生血管性年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)(湿)。
药理:
Aflibercept是一种重组人血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)受体1和2外域融合人IgG1的Fc部分作为玻璃体管理等渗的解决方案制定部分组成的融合蛋白。
血管内皮生长因子(VEGF - A)和胎盘生长因子(PIGF)的血管生成因子,可作为有丝分裂,趋化和内皮细胞的血管通透性因子VEGF家族成员。血管内皮生长因子通过两种受体酪氨酸激酶,VEGFR - 1和VEGFR - 2,内皮细胞表面上的行为。 PIGF只约束VEGFR - 1,白细胞表面上这也是目前。 VEGF - A的激活这些受体可以导致新生血管形成和血管通透性。
Aflibercept行为作为一种可溶性的诱饵受体的结合VEGF - A和PIGF,从而可以抑制这些同源的血管内皮生长因子受体的结合和激活。
临床试验:
在两项随机,多中心,双盲,主动控制的研究与AMD患者的Eylea的安全性和疗效进行了评估。在这两项研究(View1和View2中),共有2412与患者的青睐范围从49-99年,平均76岁,治疗和疗效(Eylea 1817)评估。
在每个研究中,患者被随机分配在一个1:1:1:1的比例4给药方案1:1)Eylea管理2毫克每8个星期以下3个初始每月剂量(EYLEA 2Q8); 2)Eylea管理2毫克,每4周(EYLEA 2Q4); 3)Eylea管理0.5mg的每4个星期(EYLEA 0.5Q4);和4)兰尼管理0.5mg的,每4周(兰尼0.5mg的第四季度)。
在这两项研究中,主要疗效终点的患者比例保持视力的人,定义为失去视力少于15个字母与基线相比,52周时。 EYLEA 2Q8和EYLEA 2Q4组有疗效,临床相当于0.5mg的第四季度集团兰尼。
法律分类:
接收
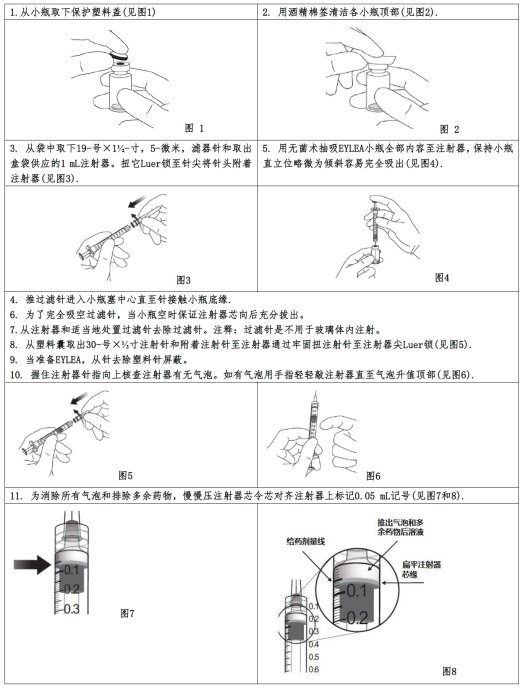
成人:
给予玻璃体内注射。 2毫克(0.05mL),每4周一次(每月)为第3个月,每8周一次2毫克(0.05mL)。
儿童:
不成立的。
禁忌(S):
眼或眼周感染。积极眼内炎症。
警告/注意事项:
动脉血栓栓塞事件的潜在风险(例如,非致死性卒中或心肌梗死,血管性死亡)。监视器在一周注射后眼内炎和视网膜脱离。注射后的视神经头监视眼压和灌注。怀孕(Cat.C)。哺乳的母亲:不推荐。
不良反应(S):
结膜下出血,眼睛疼痛,白内障,玻璃体后脱离,玻璃体飞蚊症,眼压增高,结膜充血,角膜糜烂,注射部位疼痛,异物感,眼。
注:
政府由眼科玻璃体内注射的合格医生。过程应控制无菌条件下进行。注射前,应给予适当的麻醉和外用广谱杀微生物。
如何提供:
单眼用小瓶- 1(W.针头注射器)
最后更新:
2011年12月9日

小瓶
玻璃小瓶只为单次使用。
阿柏西普获准治老年黄斑变性
2011年11月18日,美国食品与药物管理局(FDA)批准Eylea(阿柏西普,aflibercept) 治疗有新生血管的年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD),该病是美国60岁以上人群视力丧失和致盲的首要原因。
两项纳入2412例成年患者的临床试验评价了Eylea的安全性和有效性。参试者接受Eylea或Lucentis(雷珠单抗注射)治疗。两研究的主要终点是治疗一年后病人视力的视敏度。
每4周或每8周,Eylea由眼科医师注入病人眼内。研究显示,在维持或改善视敏度方面,Eylea与Lucentis同样有效。
接受Eylea病人最常见的副作用包括眼痛、结膜出血、玻璃体漂浮物、白内障和眼压增高。
FDA告诫,Eylea不应用于有活动性眼部感染或有眼内活动性炎症的病人。Eylea尚未在妊娠妇女中进行研究,所以,只有当治疗的潜在益处超过潜在风险时才能用于妊娠妇女。年龄相关的黄斑变性不出现在儿童,Eylea未在儿童中进行研究。
EYLEA
Manufacturer:
Regeneron
Pharmacological Class:
Recombinant fusion protein (human VEGF inhibitor + human IgG1).
Active Ingredient(s):
Aflibercept 40mg/mL; soln for oph intravitreal inj; preservative-free.
Indication(s):
Treatment of neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Pharmacology:
Aflibercept is a recombinant fusion protein consisting of portions of human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors 1 and 2 extracellular domains fused to the Fc portion of human IgG1 formulated as an iso-osmotic solution for intravitreal administration.
Vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and placental growth factor (PIGF) are members of the VEGF family of angiogenic factors that can act as mitogenic, chemotactic, and vascular permeability factors for endothelial cells. VEGF acts via two receptor tyrosine kinases, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, present on the surface of endothelial cells. PIGF binds only to VEGFR-1, which is also present on the surface of leucocytes. Activation of these receptors by VEGF-A can result in neovascularization and vascular permeability.
Aflibercept acts as a soluble decoy receptor that binds VEGF-A and PIGF, and thereby can inhibit the binding and activation of these cognate VEGF receptors.
Clinical Trials:
The safety and efficacy of Eylea were evaluated in two randomized, multi-center, double-masked, active-controlled studies in patients with AMD. In the two studies (VIEW1 and VIEW2), a total of 2,412 patients with ages ranged from 49–99 years with a mean of 76 years were treated and evaluable for efficacy (1,817 with Eylea).
In each study, patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to 1 of 4 dosing regimens: 1) Eylea administered 2mg every 8 weeks following 3 initial monthly doses (EYLEA 2Q8); 2) Eylea administered 2mg every 4 weeks (EYLEA 2Q4); 3) Eylea administered 0.5mg every 4 weeks (EYLEA 0.5Q4); and 4) ranibizumab administered 0.5mg every 4 weeks (ranibizumab 0.5mg Q4).
In both studies, the primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients who maintained vision, defined as losing fewer than 15 letters of visual acuity at week 52 compared to baseline. Both EYLEA 2Q8 and EYLEA 2Q4 groups were shown to have efficacy that was clinically equivalent to the ranibizumab 0.5mg Q4 group.
Legal Classification:
Rx
Adults:
Give by intravitreal inj. 2mg (0.05mL) once every 4 weeks (monthly) for the 1st 3 months, followed by 2mg (0.05mL) once every 8 weeks.
Children:
Not established.
Contraindication(s):
Ocular or periocular infections. Active intraocular inflammation.
Warnings/Precautions:
Potential risk of arterial thromboembolic events (eg, nonfatal stroke or MI, vascular death). Monitor for endophthalmitis and retinal detachments during the week following injection. Monitor intraocular pressure and perfusion of optic nerve head after injection. Pregnancy (Cat.C). Nursing mothers: not recommended.
Adverse Reaction(s):
Conjunctival hemorrhage, eye pain, cataract, vitreous detachment, vitreous floaters, increased intraocular pressure, conjunctival hyperemia, corneal erosion, inj site pain, foreign body sensation in eye.
Notes:
Administration by a qualified physician for ophthalmic intravitreal injection only. Procedure should be carried out under controlled aseptic conditions. Adequate anesthesia and a topical broad-spectrum microbicide should be given prior to the injection.
How Supplied:
Single eye use vial—1 (w. needles + syringe)
Eylea获准用于治疗黄斑变性
美国食品药品管理局(FDA)和Regeneron公司宣布Eylea(阿柏西普)已获准用于治疗新生血管性(湿性)年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)。
Eylea是一种重组融合蛋白,由人血管内皮细胞生长因子(VEGF)受体1和2的胞外区与人免疫球蛋白G1的可结晶片段融合而成,其制剂为等渗溶液。Eylea可与VEGF-A和胎盘生长因子相结合,起可溶性诱骗受体的作用,因此能够抑制这些同源性VEGF受体的结合和活化。据Regeneron公司称,VEGF是一种天然蛋白,其在健康机体内的正常作用为激活血管新生过程,支持机体组织和器官的生长。不过在湿性AMD等某些疾病中,VEGF还与眼内异常新生血管的生长有关,表现为血管通透性异常增加,进而形成水肿,常可导致结痂和高分辨率的中心视力丧失。
Eylea的安全性和疗效已在2项针对湿性AMD患者的随机、多中心、双盲、阳性对照研究中得到了评估。共有2,412例患者接受治疗并可进行疗效评估(其中1,817例接受Eylea治疗),年龄介于49~99岁,平均年龄为76岁。在这2项研究中,患者均按照1:1:1:1的比例被随机分配至以下4种给药方案组之一:
Eylea 2 mg,开始为每月给药1次,持续3次,随后改为每8周给药1次(Eylea 2Q8);
Eylea 2 mg,每4周给药1次(Eylea 2Q4);
Eylea 0.5 mg,每4周给药1次(Eylea 0.5Q4);
雷珠单抗 0.5 mg,每4周给药1次(雷珠单抗 0.5Q4)。
这2项研究的主要疗效终点均为维持视力不变的患者比例,定义为第52周时视敏度较基线下降少于15个字母。就该主要终点而言,Eylea 2Q8和2Q4治疗组与雷珠单抗 0.5Q4治疗组在临床上等效。
接受Eylea治疗的患者中报告最多的不良反应是结膜出血、眼痛、白内障、玻璃体脱离、飞蚊症以及眼内压增高。使用玻璃体内注射Eylea等VEGF抑制剂后存在发生动脉血栓栓塞性事件的潜在风险,这类事件被定义为非致死性卒中、非致死性心肌梗死或血管性死亡(包括不明原因的死亡)。在临床试验中Eylea治疗组的这类事件发生率很低。
Eylea的建议剂量为2 mg,经玻璃体内注射给药,前12周每4周给药1次,而后改为每8周给药1次。尽管Eylea的给药频率可达到2 mg、每4周给药1次,但研究表明,与每8周给药1次相比,这种方案的疗效并未增加。

|






