|
英文药名: Imuran(Azathioprine Tablets) 中文药名: 依木兰(硫唑嘌呤片)
药品名称 英文药名: Imuran (Azathioprine Tablets) (品牌)生产厂家: Glaxo Smith Kline 葛兰素史克 本药是6-硫基嘌呤的咪唑衍生物,为具有免疫抑制作用的抗代谢剂。可产生烷基化作用阻断SH组群,抑制核酸的生物合成,防止细胞的增生,并可引起DNA的损害。动物实验证实,本药可使胸腺、脾内DNA、RNA减少,影响DNA、RNA,以及蛋白质的合成,主要抑制T-淋巴细胞而影响免疫,所以可抑制迟发过敏反应,器官移植的排斥反应。本药的疗效需于治疗数周或数月后才出现。在上消化道内吸收较佳。血浆中的硫唑嘌呤及6-硫基嘌呤水平与本药的疗效及毒性无相互关系。 本药可致染色体异常,动物实验表明可致不同程度的胎儿异常,并具有明显的致畸性,不能排除本药对人体的致癌性。 本药与其它药物联合应用于器官移植病人的抗排斥反应,例如肾移植、心脏移植及肝移植,亦减少肾移植受者对皮质激素的需求。本药也可单独使用于严重的风湿性关节炎,系统性红斑狼疮,皮肌炎/多发性肌炎,自体免疫性慢性活动性肝炎,寻常天疱疮,结节性多动脉炎,自体免疫性溶血性贫血,慢性顽固自发性血小板减少性紫癜。 *注射剂只有在无法口服时才由静脉给药,且当口服疗法可以耐受时即应停用。 过敏反应:如全身不适、头晕、恶心、呕吐、腹泻、发热、寒战、肌痛、关节痛、肝功能异常和低血压。应立即停药和给予支持疗法,可使大部分病例恢复。 对本药及6-疏基嘌呤过敏者禁用。 在治疗的首8周内,至少每周检查1次全血象,包括血小板。如使用大剂量或病人有肝和/或肾功能不全时,血象检查的次数应该更多。此后每月或最少每3个月重复进行全血象的检查。 临床上证明本药对胎儿有不良影响,只有对孕妇的益处大于对胎儿产生的危险时,才可考虑使用。本药可分泌入乳汁,故哺乳妇女慎用。 别嘌呤醇可抑制巯基嘌呤(后者是硫唑嘌呤的活性代谢物)代谢成无活性产物,结果使巯基嘌呤的毒性增加,当二者必须同时服用时,硫唑嘌呤的剂量应该大大地减低,硫唑嘌呤可降低6-巯嘌呤的灭活率,6-巯嘌呤的灭活通过下列方式:酶的S-甲基化,与酶无关的氧化,或是被黄嘌呤氧化酶转变成硫尿酸盐等。硫唑嘌呤能与巯基化合物如谷胱甘肽起反应,在组织中缓缓释出6-巯嘌呤而起到前体药物的作用。 症状 Imuran™ 依木蘭™ Azathioprine
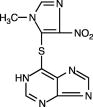
Imuran™ Injection 50mg 1 vial Imuran™ Tablets 50mg 100's Imuran™ Tablets 25mg 100's IMURAN® (azathioprine) WARNING DESCRIPTION Azathioprine is chemically 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)thio]-1H-purine. The structural formula of azathioprine is: It is an imidazolyl derivative of 6-mercaptopurine and many of its biological effects are similar to those of the parent compound. Azathioprine is insoluble in water, but may be dissolved with addition of one molar equivalent of alkali. The sodium salt of azathioprine is sufficiently soluble to make a 10mg/mL water solution which is stable for 24 hours at 59° to 77°F (15° to 25°C). Azathioprine is stable in solution at neutral or acid pH but hydrolysis to mercaptopurine occurs in excess sodium hydroxide (0.1N), especially on warming. Conversion to mercaptopurine also occurs in the presence of sulfhydryl compounds such as cysteine, glutathione, and hydrogen sulfide. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Azathioprine is metabolized to 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP). Both compounds are rapidly eliminated from blood and are oxidized or methylated in erythrocytes and liver; no azathioprine or mercaptopurine is detectable in urine after 8 hours. Activation of 6-mercaptopurine occurs via hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) and a series of multi-enzymatic processes involving kinases to form 6-thioguanine nucleotides (6-TGNs) as major metabolites (See Metabolism Scheme in Figure 1). The cytotoxicity of azathioprine is due, in part, to the incorporation of 6-TGN into DNA. 6-MP undergoes two major inactivation routes (Figure 1). One is thiol methylation, which is catalyzed by the enzyme thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT), to form the inactive metabolite methyl-6-MP (6-MeMP). TPMT activity is controlled by a genetic polymorphism.1, 2, 3 For Caucasians and African Americans, approximately 10% of the population inherit one non-functional TPMT allele (heterozygous) conferring intermediate TPMT activity, and 0.3% inherit two TPMT non-functional alleles (homozygous) for low or absent TPMT activity. Non-functional alleles are less common in Asians. TPMT activity correlates inversely with 6-TGN levels in erythrocytes and presumably other hematopoietic tissues, since these cells have negligible xanthine oxidase (involved in the other inactivation pathway) activities, leaving TPMT methylation as the only inactivation pathway. Patients with intermediate TPMT activity may be at increased risk of myelotoxicity if receiving conventional doses of IMURAN. Patients with low or absent TPMT activity are at an increased risk of developing severe, life-threatening myelotoxicity if receiving conventional doses of IMURAN.4-9 TPMT genotyping or phenotyping (red blood cell TPMT activity) can help identify patients who are at an increased risk for developing IMURAN toxicity.2, 3, 7, 8, 9 Accurate phenotyping (red blood cell TPMT activity) results are not possible in patients who have received recent blood transfusions. See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions, PRECAUTIONS: Laboratory Tests and ADVERSE REACTIONS sections. Figure 1. Metabolism pathway of azathioprine: competing pathways result in inactivation by TPMT or XO, or incorporation of cytotoxic nucleotides into DNA. Another inactivation pathway is oxidation, which is catalyzed by xanthine oxidase (XO) to form 6-thiouric acid. The inhibition of xanthine oxidase in patients receiving allopurinol (ZYLOPRIM®) is the basis for the azathioprine dosage reduction required in these patients (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions). Proportions of metabolites are different in individual patients, and this presumably accounts for variable magnitude and duration of drug effects. Renal clearance is probably not important in predicting biological effectiveness or toxicities, although dose reduction is practiced in patients with poor renal function. INDICATIONS AND USAGE CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS Serious infections are a constant hazard for patients receiving chronic immunosuppression, especially for homograft recipients. Fungal, viral, bacterial, and protozoal infections may be fatal and should be treated vigorously. Reduction of azathioprine dosage and/or use of other drugs should be considered. IMURAN is mutagenic in animals and humans, carcinogenic in animals, and may increase the patient's risk of neoplasia. Renal transplant patients are known to have an increased risk of malignancy, predominantly skin cancer and reticulum cell or lymphomatous tumors. The risk of post-transplant lymphomas may be increased in patients who receive aggressive treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. The degree of immunosuppression is determined, not only by the immunosuppressive regimen, but also by a number of other patient factors. The number of immunosuppressive agents may not necessarily increase the risk of post-transplant lymphomas. However, transplant patients who receive multiple immunosuppressive agents may be at risk for over-immunosuppression; therefore, immunosuppressive drug therapy should be maintained at the lowest effective levels. Information is available on the spontaneous neoplasia risk in rheumatoid arthritis, and on neoplasia following immunosuppressive therapy of other autoimmune diseases. It has not been possible to define the precise risk of neoplasia due to IMURAN. The data suggest the risk may be elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, though lower than for renal transplant patients. However, acute myelogenous leukemia as well as solid tumors have been reported in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have received azathioprine. Data on neoplasia in patients receiving IMURAN can be found under ADVERSE REACTIONS. IMURAN has been reported to cause temporary depression in spermatogenesis and reduction in sperm viability and sperm count in mice at doses 10 times the human therapeutic dose;10 a reduced percentage of fertile matings occurred when animals received 5 mg/kg. 11 PRECAUTIONS
* Data on the rate and risk of neoplasia among persons with rheumatoid arthritis treated with azathioprine are limited. The incidence of lymphoproliferative disease in patients with RA appears to be significantly higher than that in the general population. In one completed study, the rate of lymphoproliferative disease in RA patients receiving higher than recommended doses of azathioprine (5 mg/kg per day) was 1.8 cases per 1000 patient-years of follow-up, compared with 0.8 cases per 1000 patient-years of follow-up in those not receiving azathioprine. However, the proportion of the increased risk attributable to the azathioprine dosage or to other therapies (i.e., alkylating agents) received by patients treated with azathioprine cannot be determined. OVERDOSAGE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F) in a dry place and protect from light. 20-mL vial, each containing the equivalent of 100 mg azathioprine (as the sodium salt) (NDC 65483-551-01). Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F) and protect from light. The sterile, lyophilized sodium salt is yellow, and should be dissolved in Sterile Water for Injection |