|
2012年8月3日,美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准Zaltrap(ziv-aflibercept)为与一种FOLFIRI (叶酸[folinic acid],氟尿嘧啶[fluorouracil]和伊立替康[irinotecan])化疗方案联用治疗结肠直肠癌成年。
Special populations Older people In the pivotal MCRC study, 28.2% of patients were aged ≥65 and <75 and 5.4% of patients were aged ≥75. No dose adjustments of ZALTRAP is required in the older people. Hepatic impairment There have been no formal studies with ZALTRAP in patients with hepatic impairment (see section 5.2). Clinical data suggest that no change in aflibercept dose is required in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. There are no data regarding the administration of aflibercept in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Renal impairment There have been no formal studies with ZALTRAP in patients with renal impairment (see section 5.2). Clinical data suggest that no change in starting dose is required in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. There are very limited data in patients with severe renal impairment; therefore, these patients should be treated with caution. Paediatric population There is no relevant use of ZALTRAP in the paediatric population for the indication of metastatic colorectal cancer. Method of administration ZALTRAP is to be administered only as an intravenous infusion over 1 hour. Due to hyperosmolality (1000 mOsmol/kg) of the ZALTRAP concentrate, undiluted ZALTRAP concentrate must not be administered as an intravenous push or bolus. ZALTRAP must not be administered as an intravitreal injection (see sections 4.3 and 4.4). Each vial of concentrate for solution for infusion is for single use (single-dose) only. Diluted solutions of ZALTRAP should be administered using infusion sets containing a 0.2 micron polyethersulfone filter. The infusion sets should be made of one of the following materials: • polyvinyl chloride (PVC) containing bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) • DEHP free PVC containing trioctyl-trimellitate (TOTM) • polypropylene • polyethylene lined PVC • polyurethane Filters made of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) or nylon must not be used. Precautions to be taken before handling or administering the medicinal product For instructions on dilution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.6. 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to aflibercept or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. Ophthalmic/intravitreal use due to hyperosmotic properties of ZALTRAP (see section 4.4). For contraindications related to FOLFIRI components (irinotecan, 5-FU, and folinic acid), refer to the current respective summary of product characteristics. 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Haemorrhage An increased risk of haemorrhage, including severe and sometimes fatal haemorrhagic events has been reported in patients treated with aflibercept (see section 4.8). Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of GI bleeding and other severe bleeding. Aflibercept should not be administered to patients with severe haemorrhage (see section 4.2). Thrombocytopenia has been reported in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. Monitoring of complete blood count (CBC) with platelets is recommended at baseline, prior to initiation of each cycle of aflibercept, and as clinically necessary. Administration of the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI should be delayed until platelet count is ≥75 x 109/L (see section 4.2). Gastrointestinal perforation GI perforation including fatal GI perforation has been reported in patients treated with aflibercept (see section 4.8). Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of GI perforation. Aflibercept treatment should be discontinued in patients who experience GI perforation (see section 4.2). Fistula formation Fistula formation involving GI and non-GI sites has occurred in patients treated with aflibercept (see section 4.8). Aflibercept treatment should be discontinued in patients who develop fistula (see section 4.2). Hypertension An increased risk of grade 3-4 hypertension (including hypertension and one case of essential hypertension) has been observed in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.8). Pre-existing hypertension must be adequately controlled before starting aflibercept. If hypertension cannot be adequately controlled, treatment with aflibercept should not be initiated. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure every two weeks, including before each administration or as clinically indicated during treatment with aflibercept. In the event of hypertension on aflibercept treatment, blood pressure should be controlled with appropriate anti-hypertensive therapy and blood pressure should be monitored regularly. In case of recurrent medically significant or severe hypertension, despite optimal treatment, aflibercept should be suspended until the hypertension is controlled and the aflibercept dose should be reduced to 2 mg/kg for subsequent cycles. Aflibercept should be permanently discontinued if hypertension cannot be adequately managed with appropriate anti hypertensive therapy or aflibercept dose reduction, or if hypertensive crisis or hypertensive encephalopathy occurs (see section 4.2). Hypertension may exacerbate underlying cardiovascular disease. Caution should be exercised when treating patients with history of clinically significant cardiovascular disease such as coronary artery disease, or congestive heart failure with ZALTRAP. Patients with NYHA class III or IV congestive heart failure should not be treated with ZALTRAP. Thrombotic and embolic events Arterial thromboembolic events (ATE) ATE (including transient ischaemic attack, cerebrovascular accident, angina pectoris, intracardiac thrombus, myocardial infarction, arterial embolism, and ischaemic colitis) have been observed in patients treated with aflibercept (see section 4.8). Aflibercept treatment should be discontinued in patients who experience an ATE (see section 4.2). Venous thromboembolic events (VTE) VTE including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (infrequently fatal) have been reported in patients treated with aflibercept (see section 4.8). ZALTRAP should be discontinued in patients with life-threatening (Grade 4) thromboembolic events (including pulmonary embolism) (see section 4.2). Patients with Grade 3 DVT should be treated with anticoagulation as clinically indicated, and aflibercept therapy should be continued. In the event of recurrence, despite appropriate anticoagulation, aflibercept treatment should be discontinued. Patients with thromboembolic events of Grade 3 or lower need to be closely monitored. Proteinuria Severe proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, and thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) have been observed in patients treated with aflibercept (see section 4.8). Proteinuria should be monitored by urine dipstick analysis and/or urinary protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) for the development or worsening of proteinuria before each aflibercept administration. Patients with a dipstick of ≥2+ for protein or a UPCR >1 should undergo a 24-hour urine collection. Aflibercept administration should be suspended for ≥2 grams of proteinuria/24 hours and restarted when proteinuria is <2 grams/24 hours. If there is recurrence, the administration should be suspended until <2 grams/24 hours and then the dose reduced to 2 mg/kg. Aflibercept treatment should be discontinued in patients who develop nephrotic syndrome or TMA (see section 4.2). Neutropenia and neutropenic complications A higher incidence of neutropenic complications (febrile neutropenia and neutropenic infection) has been observed in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.8). Monitoring of complete blood count (CBC) with differential count is recommended at baseline and prior to initiation of each cycle of aflibercept. Administration of ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI should be delayed until neutrophil count is ≥1.5 x 109/L (see section 4.2). Therapeutic use of G-CSF at first occurrence of grade ≥3 neutropenia and secondary prophylaxis may be considered in patients who may be at increased risk for neutropenia complications. Diarrhoea and dehydration A higher incidence of severe diarrhoea has been observed in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.8). Dose modification of FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.2), anti-diarrhoeal medicinal products, and rehydration as needed should be instituted. Hypersensitivity reactions In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, severe hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.8). In the event of a severe hypersensitivity reaction (including bronchospasm, dyspnoea, angioedema, and anaphylaxis), aflibercept should be discontinued and appropriate medical measures should be administered (see section 4.2). In the event of a mild to moderate hypersensitivity reaction to ZALTRAP (including flushing, rash, urticaria, and pruritus), aflibercept should be temporarily suspended until the reaction is resolved. Treatment with corticosteroids and/or antihistamines can be initiated as clinically indicated. Pre-treatment with corticosteroids and/or antihistamines may be considered in subsequent cycles (see section 4.2). Caution should be used when retreating patients with prior hypersensitivity reactions as recurrent hypersensitivity reactions have been observed in some patients despite prophylaxis, including corticosteroids. Compromised wound healing Aflibercept impaired wound healing in animal models (see section 5.3). Potential for compromised wound healing (wound dehiscence, anastomotic leakage) has been reported with aflibercept (see section 4.8). Aflibercept should be suspended for at least 4 weeks prior to elective surgery. It is recommended that aflibercept not be initiated for at least 4 weeks following major surgery and not until the surgical wound is fully healed. For minor surgery such as central venous access port placement, biopsy, and tooth extraction, aflibercept may be initiated/restarted once the surgical wound is fully healed. Aflibercept should be discontinued in patients with compromised wound healing requiring medical intervention (see section 4.2). Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) PRES was not reported in the pivotal phase III study of MCRC patients. In other studies, PRES was reported in patients treated with aflibercept as monotherapy and in combination with other chemotherapies (see section 4.8). PRES may present with altered mental status, seizure, nausea, vomiting, headache, or visual disturbances. The diagnosis of PRES is confirmed by brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Aflibercept should be discontinued in patients that develop PRES (see section 4.2). Older people Older people patients ≥65 years had an increased risk of diarrhoea, dizziness, asthenia, weight loss and dehydration. Careful monitoring is recommended in order to rapidly detect and treat signs and symptoms of diarrhoea and dehydration and to minimize potential risk (see section 4.8). Renal impairment There are very limited data available for patients with severe renal impairment treated with aflibercept. No dose adjustment is required for aflibercept (see sections 4.2, 4.8 and 5.2). Performance status and co-morbidities Patients with ECOG performance status ≥2 or having significant co-morbidities may be at greater risk for a poor clinical outcome and should be carefully monitored for early clinical deterioration. Off-label intravitreal use ZALTRAP is a hyperosmotic solution, which is not formulated for compatibility with the intraocular environment. ZALTRAP must not be administered as an intravitreal injection (see section 4.3). 4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Population pharmacokinetics analysis and inter study comparisons did not reveal any pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction between aflibercept and the FOLFIRI regimen. 4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation Women of childbearing potential / Contraception in males and females Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while on ZALTRAP, and should be informed of the potential hazard to the foetus. Women of childbearing potential and fertile males should use effective contraception during and up to a minimum of 6 months after the last dose of treatment. Pregnancy There are no data from the use of aflibercept in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3). As angiogenesis is critical to foetal development, the inhibition of angiogenesis following administration of ZALTRAP may result in adverse effects on pregnancy. ZALTRAP should be used only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk during pregnancy. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking ZALTRAP, she should be informed of the potential hazard to the foetus. Breast-feeding No studies have been conducted to assess the impact of ZALTRAP on milk production, its presence in breast milk or its effects on the breast-fed child. It is unknown whether aflibercept is excreted in human milk. A risk to the newborns/infants cannot be excluded. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from ZALTRAP therapy taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman. Fertility Male and female fertility are likely to be compromised during treatment with aflibercept based on studies in monkeys (see section 5.3). 4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines ZALTRAP has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines. If patients are experiencing symptoms that affect their vision or concentration, or their ability to react, they should be advised not to drive or use machines (see section 4.8). 4.8 Undesirable effects Summary of the safety profile The safety of ZALTRAP in combination with FOLFIRI was evaluated in 1216 patients previously treated for metastatic colorectal cancer, of which 611 patients were treated with ZALTRAP 4 mg/kg every two weeks (one cycle) and 605 patients were treated with placebo/FOLFIRI in a phase III study. Patients received a median number of 9 cycles of the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. The most common adverse reactions (all grades, ≥20% incidence) reported at least 2% greater incidence for the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen as compared to the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen in order of decreasing frequency were leucopenia, diarrhoea, neutropenia, proteinuria, increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), stomatitis, fatigue, thrombocytopenia, increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypertension, weight loss, decreased appetite, epistaxis, abdominal pain, dysphonia, increased serum creatinine, and headache (see Table 1). The most common reported grades 3-4 reactions (≥5% incidence) reported at least 2% greater incidence for the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen as compared to the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen in order of decreasing frequency, were neutropenia, diarrhoea, hypertension, leucopenia, stomatitis, fatigue, proteinuria, and asthenia (see Table 1). The most frequent adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation in ≥1% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen were vascular disorders (3.8%) including hypertension (2.3%), infections (3.4%), asthenia/fatigue (1.6%, 2.1%),diarrhoea (2.3%), dehydration (1%), stomatitis (1.1%), neutropenia (1.1%), proteinuria (1.5%), and pulmonary embolism (1.1%). Tabulated summary of adverse reactions Adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities reported in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen are listed in Table 1 according to MedDRA system organ class and frequency categories. Adverse reactions in Table 1 are defined as either any adverse clinical reaction or laboratory abnormality having ≥2% greater incidence (all grades) in the aflibercept treatment group in comparison to the placebo treatment group in the MCRC study including those that do not meet this threshold but were consistent with the anti-VEGF class and were seen in any study with aflibercept. Intensity of the adverse reactions is graded according to NCI CTC version 3.0 (grade ≥3 = G≥3). Frequencies are based on all grades and defined as: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Table 1 - Adverse reactions reported in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen from the MCRC study
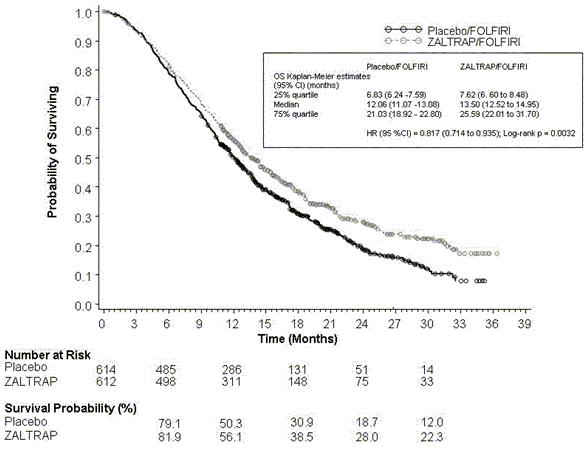
Description of selected adverse reactions Haemorrhage Patients treated with ZALTRAP have an increased risk of haemorrhage, including severe and sometimes fatal haemorrhagic events. In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, episodes of bleeding/haemorrhage (all grades) was reported in 37.8% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 19.0% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. The most common reported form of bleeding was minor (grade 1-2) epistaxis occurring in 27.7% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 haemorrhage including GI haemorrhage, haematuria, and post-procedural haemorrhage was reported in 2.9% of patients receiving the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared with 1.7% of patients receiving the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. In other studies, severe intracranial haemorrhage and pulmonary haemorrhage/haemoptysis including fatal events have occurred in patients receiving ZALTRAP (see section 4.4). Gastrointestinal perforation GI perforation including fatal GI perforation has been reported in patients treated with ZALTRAP. In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, GI perforation (all grades) was reported in 3 of 611 patients (0.5%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 3 of 605 patients (0.5%) treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 GI perforation events occurred in all 3 patients (0.5%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and in 2 patients (0.3%) treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Across the three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancer populations), the incidence of GI perforation (all grades) was 0.8% for patients treated with ZALTRAP and 0.3% for patients treated with placebo. Grade 3-4 GI perforation events occurred in 0.8% of patients treated with ZALTRAP and 0.2% of patients treated with placebo (see section 4.4). Fistula formation Fistula formation involving GI and non-GI sites has occurred in patients treated with ZALTRAP. In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, fistulas (anal, enterovesical, enterocutaneous, colovaginal, intestinal sites) were reported in 9 of 611 patients (1.5%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 3 of 605 patients (0.5%) treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3 GI fistula formation occurred in 2 patients treated with ZALTRAP (0.3%) and in 1 placebo-treated patient (0.2%). Across the three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancer populations), the incidence of fistula (all grades) was 1.1% for patients treated with ZALTRAP and 0.2% for patients treated with placebo. Grade 3-4 fistula occurred in 0.2% of patients treated with ZALTRAP and 0.1% of patients treated with placebo (see section 4.4). Hypertension In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, hypertension (all grades) has been reported in 41.2% of patients treated with ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI and 10.7% of patients treated with placebo/FOLFIRI. An increased risk of grade 3-4 hypertension (including hypertension and one case of essential hypertension) has been observed in patients receiving the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3 hypertension (requiring adjustment in existing anti-hypertensive therapy or treatment with more than one medicinal product) was reported in 1.5% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen and 19.1% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 4 hypertension (hypertensive crisis) was reported in 1 patient (0.2%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. Among those patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen developing grade 3-4 hypertension, 54% had onset during the first two cycles of treatment (see section 4.4). Thrombotic and embolic events Arterial thromboembolic events In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, ATE (including transient ischaemic attack, cerebrovascular accident, angina pectoris, intracardiac thrombus, myocardial infarction, arterial embolism, and ischaemic colitis) were reported in 2.6% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 1.5% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 events occurred in 11 patients (1.8%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 3 patients (0.5%) treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Across the three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancer populations), the incidence of ATE (all grades) was 2.3% for patients treated with ZALTRAP and 1.7% for patients treated with placebo. Grade 3-4 ATE occurred in 1.7% of patients treated with ZALTRAP and 1.0% of patients treated with placebo (see section 4.4). Venous thromboembolic events Venous thromboembolic events (VTE) include deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, all grades VTE occurred in 9.3% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 7.3% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 VTE occurred in 7.9% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and in 6.3% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Pulmonary embolism occurred in 4.6% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 3.5% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Across the three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancer populations), the incidence of VTE (all grades) was 7.1% for patients treated with ZALTRAP and 7.1% for patients treated with placebo. Proteinuria In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, proteinuria (compiled from clinical and laboratory data) was reported in 62.2% patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 40.7% patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 proteinuria occurred in 7.9% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 1.2% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Nephrotic syndrome occurred in 2 patients (0.5%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to none of the patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. One patient treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen presenting with proteinuria and hypertension was diagnosed with thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). Across the three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancer populations), the incidence of nephrotic syndrome was 0.5% of patients treated with ZALTRAP and 0.1% of patients treated with placebo (see section 4.4). Neutropenia and neutropenic complications In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, neutropenia (all grades) has been reported in 67.8% of patients treated with ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI and 56.3% of patients treated with placebo/FOLFIRI. Grade 3-4 neutropenia was observed in 36.7% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 29.5% patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. The most common grade 3-4 neutropenic complication was the occurrence of febrile neutropenia in 4.3% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 1.7% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 neutropenic infection/sepsis occurred in 1.5% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 1.2% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.4). Infections Infections occurred at a higher frequency in patients receiving the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen (46.2%, all grades; 12.3%, grade 3-4) than in patients receiving the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen (32.7%, all grades; 6.9%, grade 3-4), including urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, catheter site infection, and tooth infection. Diarrhoea and dehydration In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, diarrhoea (all grades) has been observed in 69.2% of patients treated with ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI and 56.5% of patients treated with placebo/FOLFIRI. Dehydration (all grades) has been observed in 9.0% of patients treated with ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI and 3.0% of patients treated with placebo/FOLFIRI. Grade 3-4 diarrhoea was reported in 19.3% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 7.8% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3-4 dehydration was reported in 4.3% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen compared to 1.3% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.4). Hypersensitivity reactions In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, severe hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in 0.3% of patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 0.5% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen (see section 4.4). Compromised wound healing Treatment with ZALTRAP is associated with potential for compromised wound healing (wound dehiscence, anastomotic leakage). In the pivotal study for MCRC, compromised wound healing was reported in 3 patients (0.5%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and 5 patients (0.8%) treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Grade 3 compromised wound healing was reported in 2 patients (0.3%) treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen and in none of the patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen. Across the three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancer populations), the incidence of compromised wound healing (all grades) was 0.5% for patients treated with ZALTRAP and 0.4% for patients treated with placebo. Grade 3-4 compromised wound healing occurred in 0.2% of patients treated with ZALTRAP and none of patients treated with placebo (see section 4.4). Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) PRES was not reported in the pivotal Phase III study of MCRC patients. In other studies, PRES was reported in patients treated with monotherapy ZALTRAP (0.5%) and in combination with other chemotherapies (see section 4.4). Additional adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities reported with a ≥5% difference (all grades) in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen versus the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen The following adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities were reported with a ≥5% difference (all grades) in patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen versus the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen (in order of decreasing frequency): leucopenia (78.3% versus 72.4% all grades; 15.6% versus 12.2% Grades 3-4), increased AST (57.5% versus 50.2% all grades; 3.1% versus 1.7% Grades 3-4), stomatitis (50.1% versus 32.9% all grades; 12.8% versus 4.6% Grades 3-4), fatigue (47.8% versus 39.0% all grades; 12.6% versus 7.8% Grade 3-4), thrombocytopenia (47.4% versus 33.8% all grades; 3.3% versus 1.7% Grades 3-4), increased ALT (47.3% versus 37.1% all grades; 2.7% versus 2.2% Grades 3-4), decreased appetite (31.9% versus 23.8% all grades; 3.4% versus 1.8% Grade 3-4), weight loss (31.9% versus 14.4% all grades; 2.6% versus 0.8% Grades 3-4), dysphonia (25.4% versus 3.3% all grades; 0.5% versus 0 Grades 3-4), headache (22.3% versus 8.8% all grades; 1.6% versus 0.3% Grades 3-4), asthenia (18.3% versus 13.2% all grades; 5.1% versus 3.0% Grades 3-4), Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysaesthesia syndrome (11.0% versus 4.3% all grades; 2.8% versus 0.5% Grades 3-4), and skin hyperpigmentation (8.2% versus 2.8% all grades; 0 versus 0 Grades 3-4). Paediatric population The safety in paediatric patients has not been established. Other special populations Older people Of the 611 patients treated with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen in the pivotal study of MCRC patients, 172 (28.2%) were aged ≥65 and <75 and 33 (5.4%) were age ≥75. Older people (≥65 years of age) may be more likely to experience adverse reactions. The incidence of diarrhoea, dizziness, asthenia, weight decrease, and dehydration was increased by ≥5% in older people compared to younger patients. Older people should be closely monitored for the development of diarrhoea and potential dehydration (see section 4.4). Renal impairment In patients receiving ZALTRAP, the adverse reactions in patients with mild renal impairment at baseline in three Phase III placebo-controlled clinical studies (N=352) were comparable with those of patients without renal impairment (N=642). A limited number of patients having moderate/severe renal impairment at baseline (N=49) were treated with ZALTRAP. In these patients, non-renal events were generally comparable between patients with renal impairment and those without renal impairment, except a >10% higher incidence in dehydration (all grades) was noted (see section 4.4). Immunogenicity As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity with ZALTRAP. Overall across all clinical oncology studies, similar incidence of low titre anti-drug antibody (ADA) responses (post baseline) in the ADA assay were observed in both patients treated with placebo and ZALTRAP (3.3% and 3.8%, respectively). High-titre antibody responses to aflibercept were not detected in any patients. Seventeen (17) patients treated with ZALTRAP (1.6 %) and two (2) placebo-treated patients (0.2%) were also positive in the neutralising antibody assay. In the pivotal study of MCRC patients, positive responses in the ADA assay were observed at higher levels in patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen [18/526 (3.4%)] than with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen [8/521 (1.5%)]. Positive results in the neutralising antibody assay in the MCRC pivotal study were also higher in patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen [2/526 (0.38%)] than with the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen [1/521 (0.19%)]. There was no observed impact on the pharmacokinetic profile of aflibercept in patients who were positive in the immunogenicity assays. Given the similar ADA assay results in patients treated with placebo or ZALTRAP, the actual incidence of immunogenicity with ZALTRAP based on these assays is likely to be overestimated. Immunogenicity data are highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medicinal products, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to ZALTRAP with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading. Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the Yellow Card Scheme at: www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard. 4.9 Overdose There is no information on the safety of aflibercept given at doses exceeding 7 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 9 mg/kg every 3 weeks. The most commonly observed adverse reactions at these doses were similar to those observed at the therapeutic dose. There is no specific antidote to ZALTRAP overdose. Cases of overdose should be managed by appropriate supportive measures particularly with regard to monitoring and treatment of hypertension and proteinuria. The patient should remain under close medical supervision to monitor any adverse reactions (see section 4.8). 5. Pharmacological properties 5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antineoplastic agents, other antineoplastic agents, ATC code: L01XX44 Mechanism of action Vascular endothelial growth factor A and B (VEGF-A, VEGF-B), and placental growth factor (PlGF) are members of the VEGF family of angiogenic factors that can act as potent mitogenic, chemotactic, and vascular permeability factors for endothelial cells. VEGF-A acts via two receptor tyrosine kinases, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, present on the surface of endothelial cells. PlGF and VEGF-B bind only to VEGFR-1, which is also present on the surface of leucocytes. Excessive activation of these receptors by VEGF-A can result in pathological neovascularisation and excessive vascular permeability. PlGF is also linked to pathological neovascularisation and recruitment of inflammatory cells into tumours. Aflibercept, also known as VEGF TRAP in the scientific literature, is a recombinant fusion protein consisting of VEGF-binding portions from the extracellular domains of human VEGF receptors 1 and 2 fused to the Fc portion of the human IgG1. Aflibercept is produced by recombinant DNA technology in a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) K-1 mammalian expression system. Aflibercept is a dimeric glycoprotein with a protein molecular weight of 97 kilodaltons (kDa) and contains glycosylation, constituting an additional 15% of the total molecular mass, resulting in a total molecular weight of 115 kDa. Aflibercept acts as a soluble decoy receptor that binds to VEGF-A, with higher affinity than its native receptors, as well as the related ligands PlGF and VEGF-B. By acting as a ligand trap, aflibercept prevents binding of endogenous ligands to their cognate receptors and thereby blocks receptor mediated signaling. Aflibercept blocks the activation of VEGF receptors and the proliferation of endothelial cells, thereby inhibiting the growth of new vessels that supply tumours with oxygen and nutrients. Aflibercept binds to human VEGF-A (equilibrium dissociation constant KD of 0.5 pM for VEGF-A165 and 0.36 pM for VEGF-A121), to human PlGF (KD of 39 pM for PlGF-2), and to human VEGF-B (KD of 1.92 pM) to form a stable, inert complex which has no detectable biological activity. Pharmacodynamic effects Administration of aflibercept to mice bearing xenotransplant or allotransplant tumours inhibited the growth of various cancer types. Clinical efficacy and safety The efficacy and safety of ZALTRAP were evaluated in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who had previously been treated with an oxaliplatin-based treatment with or without prior bevacizumab. A total of 1226 patients were randomised (1:1) to receive either ZALTRAP (N=612; 4 mg/kg as a 1 hour intravenous infusion on day 1) or placebo (N=614), in combination with 5-fluouracil plus irinotecan [FOLFIRI: irinotecan 180 mg/m2 intravenous infusion over 90 minutes and folinic acid (dl racemic) 400 mg/m² intravenous infusion over 2 hours at the same time on day 1 using a Y-line, followed by 5-FU 400 mg/m² intravenous bolus, followed by 5-FU 2400 mg/m² continuous intravenous infusion over 46-hours]. The treatment cycles on both arms were repeated every 2 weeks. Patients were treated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary efficacy endpoint was overall survival. Treatment assignment was stratified by the ECOG performance status (0 versus 1 versus 2) and according to prior therapy with bevacizumab (yes or no). Demographics were well balanced between the treatment arms (age, race, ECOG performance status, and prior bevacizumab status). Of the 1226 patients randomised in the study, the median age was 61 years, 58.6% were male, 97.8% had a baseline ECOG performance status (PS) of 0 or 1, and 2.2% had a baseline ECOG performance status (PS) of 2. Among the 1226 randomised patients, 89.4% and 90.2% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI and ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimens, respectively, received prior oxaliplatin-based combination chemotherapy in the metastatic/advanced setting. Approximately 10% of patients (10.4% and 9.8% of patients treated with the placebo/FOLFIRI and ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimens, respectively) received prior oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy and progressed on or within 6 months of completion of adjuvant chemotherapy. Oxaliplatin-based regimens were administered in combination with bevacizumab in 373 patients (30.4%). Overall efficacy results for the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen versus the placebo/FOLFIRI regimen are summarised in Figure 1 and Table 2. Figure 1 – Overall survival (months) – Kaplan-Meier curves by treatment group – ITT population
Table 3 - OS and PFS by prior bevacizumab exposurea – ITT population
Post-hoc analyses excluding patients who progressed during or within 6 months of adjuvant therapy for patients with or without prior bevacizumab treatment are summarised in Table 4. Table 4 - Post-hoc analyses excluding adjuvant patientsa,b
In sub-group analysis of overall survival, a benefit consistent with the overall population was observed in patients <65 years old and ≥65 years old who received the ZALTRAP/FOLFIRI regimen. Paediatric population The European Medicines Agency has waived the obligation to conduct studies with ZALTRAP in all subsets of the paediatric population in adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum (see section 4.2 for information on paediatric use). 5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties The pharmacokinetic properties described below have to a large extent been derived from a population pharmacokinetic analysis with data from 1507 patients with various types of advanced malignancies. Absorption In preclinical tumour models, biologically active doses of aflibercept correlated with those necessary to produce circulating concentrations of free aflibercept in excess of VEGF-bound aflibercept. Circulating concentrations of VEGF-bound aflibercept increase with the aflibercept dose until most available VEGF is bound. Further increases in the aflibercept dose resulted in dose-related increases in circulating free aflibercept concentrations but only small further increases in the VEGF-bound aflibercept concentration. In patients, ZALTRAP is administered at the dose of 4 mg/kg intravenously every two weeks for which there is an excess of circulating free aflibercept compared to VEGF-bound aflibercept. At the recommended dose regimen of 4 mg/kg every two weeks, concentration of free aflibercept were near steady-state levels by the second cycle of treatment with essentially no accumulation (accumulation ratio of 1.2 at steady-state compared to the first administration). Distribution The volume of distribution of free aflibercept at steady-state is approximately 8 litres. Biotransformation No metabolism studies have been conducted with aflibercept since it is a protein. Aflibercept is expected to degrade to small peptides and individual amino acids. Elimination Free aflibercept is primarily cleared by binding to endogenous VEGF to form a stable, inactive complex. As with other large proteins, both free and bound aflibercept, are expected to be cleared, more slowly, by other biological mechanisms, such as proteolytic catabolism. At doses greater than 2 mg/kg, free aflibercept clearance was approximately 1.0 L/day with a terminal half-life of 6 days. High molecular weight proteins are not cleared by the renal route, therefore renal elimination of aflibercept is expected to be minimal. Linearity/non-linearity Consistent with target-mediated drug disposition, free aflibercept exhibits a faster (non-linear) clearance at doses below 2 mg/kg, likely due to the high affinity binding of aflibercept to endogenous VEGF. Linear clearance observed in the dose range of 2 to 9 mg/kg is likely due to non saturable biological mechanisms of elimination such as protein catabolism. Other special populations Older people There was no effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of free aflibercept. Race No effect of race was identified in the population analysis. Gender Gender was the most significant covariate for explaining the interindividual variability of free aflibercept clearance and volume with a 15.5% higher clearance and a 20.6% higher volume of distribution in males than in females. These differences do not affect exposure due to weight-based dosing and no dose modifications based on gender are required. Weight Weight had an effect on free aflibercept clearance and volume of distribution resulting with a 29% increase in aflibercept exposure in patients weighing ≥100 kg. Hepatic impairment There have been no formal studies with ZALTRAP in patients with hepatic impairment. In a population pharmacokinetic analysis with data from 1507 patients with various types of advanced malignancies receiving ZALTRAP with or without chemotherapy, 63 patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.0 x – 1.5 x ULN and any AST) and 5 patients with moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5 x – 3 x ULN and any AST) were treated with ZALTRAP. In these mild and moderate hepatic impairment patients, there was no effect on clearance of aflibercept. There are no data available for patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 x ULN and any AST). Renal impairment There have been no formal studies with ZALTRAP in patients with renal impairment. A population pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted with data from 1507 patients with various types of advanced malignancies receiving ZALTRAP with or without chemotherapy. This population included; 549 patients with mild renal impairment (CLCR between 50-80 ml/min), 96 patients with moderate renal impairment (CLCR between 30-50 ml/min), and 5 patients with severe renal impairment (CLCR <30 ml/min). This population pharmacokinetic analysis revealed no clinically meaningful differences in clearance or systemic exposure (AUC) of free aflibercept in patients with moderate and mild renal impairment at the 4 mg/kg dose of ZALTRAP as compared to the overall population studied. No conclusion can be drawn for patients with severe renal impairment due to very limited data available. In the few patients with severe renal impairment, drug exposure was similar to that observed in patients with normal renal function. 5.3 Preclinical safety data Animal toxicology and pharmacology Weekly/every two weeks intravenous administration of aflibercept to cynomolgus monkeys for up to 6 months resulted in changes in the bone (effects on growth plate and the axial and appendicular skeleton), nasal cavity, kidney, ovary, and adrenal gland. Most aflibercept-related findings were noted from the lowest dose tested corresponding to plasma exposures close to those in patients at the therapeutic dose. Most aflibercept-induced effects were reversible after a 5-month drug free period with the exception of skeletal and nasal cavity findings. Most findings were considered to be related to the pharmacological activity of aflibercept. Aflibercept administration resulted in a delay in wound healing in rabbits. In full-thickness excisional and incisional skin wound models, aflibercept administration reduced fibrous response, neovascularisation, epidermal hyperplasia/re-epithelialisation, and tensile strength. Aflibercept increased blood pressure in normotensive rodents. Carcinogenesis and mutagenesis No studies have been conducted to evaluate carcinogenicity or mutagenicity of aflibercept. Impairment of fertility No specific studies with aflibercept have been conducted in animals to evaluate the effect on fertility. However, results from a repeat dose toxicity study suggest there is a potential for aflibercept to impair reproductive function and fertility. In sexually mature female cynomolgus monkeys inhibition of ovarian function and follicular development was evidenced. These animals also lost normal menstrual cycling. In sexually mature male cynomolgus monkeys a decrease in sperm motility and an increase in incidence of morphological abnormalities of spermatozoa were observed. There was no margin of exposure to patients in relation to these effects. These effects were fully reversible within 8-18 weeks after the last injection. Reproductive and developmental toxicology Aflibercept has been shown to be embryotoxic and teratogenic when administered intravenously to pregnant rabbits every 3 days during the organogenesis period (gestation days 6 to 18) at doses approximately 1 to 15 times the human dose of 4 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Observed effects included decreases in maternal body weights, an increased number of foetal resorptions, and an increased incidence of external, visceral, and skeletal foetal malformations. 6. Pharmaceutical particulars 6.1 List of excipients Sucrose Sodium chloride Sodium citrate dihydrate Citric acid monohydrate Polysorbate 20 Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) Water for injections 6.2 Incompatibilities In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products or solvents except those mentioned in section 6.6. 6.3 Shelf life Unopened vial 3 years After dilution in the infusion bag Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C and for 8 hours at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the solution for infusion should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C unless dilution has taken place in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. 6.4 Special precautions for storage Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Store in the original package in order to protect from light. For storage conditions after dilution of the medicinal product, see section 6.3. 6.5 Nature and contents of container • 4ml of concentrate in a 5 ml clear borosilicate glass vial (type I) sealed by a flanged stopper with flip-off cap and inserted coated sealing disc. Pack size of 1 vial or 3 vials. • 8ml of concentrate in a 10 ml clear borosilicate glass vial (type I) sealed by a flanged stopper with flip-off cap and inserted coated sealing disc. Pack size of 1 vial. Not all pack sizes may be marketed. 6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling ZALTRAP is a sterile, preservative-free and non-pyrogenic concentrate, therefore the solution for infusion should be prepared by a healthcare professional using safe-handling procedures and aseptic technique. Caution should be exercised when handling ZALTRAP, taking into account the use of containment devices, personal protective equipment (e.g. gloves), and preparation procedures. Preparation of the infusion solution • Inspect the ZALTRAP vial visually prior to use. The concentrate solution must be clear and without particles. • Based on the required dose for the patient, withdraw the necessary volume of ZALTRAP concentrate from the vial. More than one vial could be needed for the preparation of the infusion solution. • Dilute it to the required administration volume with sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution or 5% glucose solution for infusion. The concentration of the final ZALTRAP solution for intravenous infusion should be kept within the range of 0.6 mg/ml to 8 mg/ml of aflibercept. • PVC containing DEHP infusion bags or polyolefin infusion bags should be used. • The diluted solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discolouration prior to administration. If any discolouration or particulate matter is observed, the reconstituted solution should be discarded. • ZALTRAP is a single-use vial. Do not re-enter the vial after the initial puncture. Any unused concentrate should be discarded. Disposal Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. 7. Marketing authorisation holder sanofi-aventis groupe 54, rue La Boétie 75008 Paris France 8. Marketing authorisation number(s) EU/1/12/814/001 EU/1/12/814/003 9. Date of first authorisation/renewal of the authorisation Date of first authorisation: 01 February 2013 10. Date of revision of the text 18 December 2013 Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency http://www.ema.europa.eu
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||