|
部分中文Vitamin K1处方资料(仅供参考)
英文名称 Vitamin K1
其他名称
凝血维生素一,维生素K,维他命K1,叶绿醌,叶萘酯,植萘醌,植物甲萘醌,Konakion,Mephyton,Phytomenadione,Phytonadione,V. K1
适应证
用于维生素K缺乏或活力降低,导致凝血因子Ⅱ、Ⅶ、Ⅸ或Ⅹ合成障碍的出血性疾病。
1.新生儿出血。
2.肠道吸收不良所致维生素K缺乏。
3.广谱抗生素或肠道灭菌药致肠道内细菌合成的维生素K减少或缺乏。
4.双香豆素等抗凝剂的分子结构与维生素K相似,在体内干扰其代谢,使环氧叶绿醌不能被还原成维生素K,致体内维生素K不能发挥作用,造成与维生素K缺乏相类似的后果。
不良反应
1.静脉注射维生素K1偶尔可发生过敏样反应,曾有因快速静注而致死的报道。可出现面部潮红、出汗、支气管痉挛、心动过速以至低血压等。
2.少数可引起新生儿特别是早产儿高胆红素血症和溶血。肌内注射可引起局部红肿和疼痛。
注意事项
1.新生儿出血症以维生素K1治疗较为合适,因为其他维生素K制剂易引起高胆红素血症和溶血。
2.下列情况应引起注意:
①葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶缺陷者,补给维生素K4时应特别慎重,诱发溶血的可能;
②肝功能损伤时,维生素K的疗效不明显,凝血酶原时间极少恢复正常,如盲目大量使用维生素K,反易加重肝脏损害;
③肝索引起的出血倾向及凝血酶原时间延长,维生素K治疗无效。
3.用药期间应定期检测凝血酶原时间以调整维生素K的用量及给药次数。
药物相互作用
1.口服抗凝剂如双香豆素类可干扰维生素K代谢。两药同用,作用相互抵消。
2.较大剂量水杨酸类、磺胺类药、奎宁、硫糖铝,考来烯胺、放线菌素等也可影响维生素K的效应。
给药说明
1.维生素K有过敏反应的危险,故不宜与其他维生素制成复合剂。
2.当患者因维生素K依赖凝血因子缺乏发生严重出血时,短期应用常不足以即刻生效,可先静脉输注凝血酶原复合物、血浆或新鲜血。
3.吸收不良患者,以采用注射途径给药为宜;如仍采用口服,宜同时给予胆盐,以利吸收。
4.用于纠正口服抗凝剂引起的低凝血酶原血症时,应先用最小有效量,通过凝血酶原时间测定再调整;过多的维生素K可影响以后抗凝治疗。
用法与用量
肌内、皮下注射或静脉注射,1次10mg,每日10~20mg。
1.低凝血酶原血症不易纠正时,6~8小时后可重复注射,通常24小时内总剂量不超过40mg。由于肠道吸收不良和其他药物引起的低凝血酶原血症,成人每次肌内或皮下注射2~25mg,必要时可重复给予。仅病情严重时采用静脉注射,注药速度每分钟不超过1mg。
2.长期使用肠道外高营养液,补充维生素K,成人和儿童每周肌内注射5~10mg,婴儿肌内注射2mg。
3.新生儿出血症,肌内或皮下注射1mg,8小时后视病情需要可重复。
4.预防新生儿出血,可在婴儿出生后即肌内或皮下注射0.5~1mg,6~8小时后可重复。
制剂与规格
维生素K1注射液:①1ml:2mg;②1ml:10mg。

BOXED WARNING(What is this?)
WARNING - INTRAVENOUS USE
Severe reactions, including fatalities, have occurred during and immediately after the parenteral administration of Phytonadione. Typically these severe reactions have resembled hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis, including shock and cardiac and/or respiratory arrest. Some patients have exhibited these severe reactions on receiving Phytonadione for the first time. The majority of these reported events occurred following intravenous administration, even when precautions have been taken to dilute the Phytonadione and to avoid rapid infusion. Therefore, the INTRAVENOUS route should be restricted to those situations where another route is not feasible and the increased risk involved is considered justified.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Aqueous Colloidal Solution of Vitamin K1
Rx Only
DESCRIPTION
Phytonadione is a vitamin, which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, odorless or nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.
Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1, 4-naphthoquinone. Its empirical formula is C31H4602 and its structural formula is:
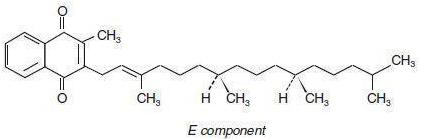
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP, is a yellow, sterile, aqueous colloidal solution of vitamin K1, with a pH of 3.5 to 7.0. It is available for injection by the intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous routes.
Each 0.5 mL contains 1 mg phytonadione (Vitamin K1), 10 mg polysorbate 80, 10.4 mg propylene glycol, 0.17 mg sodium acetate anhydrous, and 0.00002 mL glacial acetic acid. Additional glacial acetic acid or sodium acetate anhydrous may have been added to adjust pH to meet USP limits of 3.5 to 7.0. The air above the liquid in the individual containers has been displaced by flushing with nitrogen during the filling operation.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Phytonadione aqueous colloidal solution of vitamin K1 for parenteral injection, possesses the same type and degree of activity as does naturally-occurring vitamin K, which is necessary for the production via the liver of active prothrombin (factor II), proconvertin (factor VII), plasma thromboplastin component (factor IX), and Stuart factor (factor X). The prothrombin test is sensitive to the levels of three of these four factors—II, Vll, and X. Vitamin K is an essential cofactor for a microsomal enzyme that catalyzes the post-translational carboxylation of multiple, specific, peptide-bound glutamic acid residues in inactive hepatic precursors of factors II, VII, IX, and X. The resulting gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues convert the precursors into active coagulation factors that are subsequently secreted by liver cells into the blood.
Phytonadione is readily absorbed following intramuscular administration. After absorption, phytonadione is initially concentrated in the liver, but the concentration declines rapidly. Very little vitamin K accumulates in tissues. Little is known about the metabolic fate of vitamin K. Almost no free unmetabolized vitamin K appears in bile or urine.
In normal animals and humans, phytonadione is virtually devoid of pharmacodynamic activity. However, in animals and humans deficient in vitamin K, the pharmacological action of vitamin K is related to its normal physiological function, that is, to promote the hepatic biosynthesis of vitamin K dependent clotting factors.
The action of the aqueous colloidal solution, when administered intravenously, is generally detectable within an hour or two and hemorrhage is usually controlled within 3 to 6 hours. A normal prothrombin level may often be obtained in 12 to 14 hours.
In the prophylaxis and treatment of hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, phytonadione has demonstrated a greater margin of safety than that of the water-soluble vitamin K analogues.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Phytonadione is indicated in the following coagulation disorders which are due to faulty formation of factors II, VII, IX and X when caused by vitamin K deficiency or interference with vitamin K activity.
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is indicated in:
— anticoagulant-induced prothrombin deficiency caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives;
— prophylaxis and therapy of hemorrhagic disease of the newborn;
— hypoprothrombinemia due to antibacterial therapy;
— hypoprothrombinemia secondary to factors limiting absorption or synthesis of vitamin K, e.g., obstructive jaundice, biliary fistula, sprue, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, intestinal resection, cystic fibrosis of the pancreas, and regional enteritis;
— other drug-induced hypoprothrombinemia where it is definitely shown that the result is due to interference with vitamin K metabolism, e.g., salicylates.
CONTRAINDICATION
Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication.
WARNINGS
An immediate coagulant effect should not be expected after administration of phytonadione. It takes a minimum of 1 to 2 hours for measurable improvement in the prothrombin time. Whole blood or component therapy may also be necessary if bleeding is severe.
Phytonadione will not counteract the anticoagulant action of heparin.
When vitamin K1 is used to correct excessive anticoagulant-induced hypoprothrombinemia, anticoagulant therapy still being indicated, the patient is again faced with the clotting hazards existing prior to starting the anticoagulant therapy. Phytonadione is not a clotting agent, but overzealous therapy with vitamin K1 may restore conditionswhich originally permitted thromboembolic phenomena. Dosage should be kept as low as possible, and prothrombin time should be checked regularly as clinical conditions indicate.
Repeated large doses of vitamin K are not warranted in liver disease if the response to initial use of the vitamin is unsatisfactory. Failure to respond to vitamin K may indicate that the condition being treated is inherently unresponsive to vitamin K.
PRECAUTIONS
Drug InteractionsTemporary resistance to prothrombin-depressing anticoagulants may result, especially when larger doses of phytonadione are used. If relatively large doses have been employed, it may be necessary when reinstituting anticoagulant therapy to use somewhat larger doses of the prothrombin-depressing anticoagulant, or to use one which acts on a different principle, such as heparin sodium.
Laboratory TestsProthrombin time should be checked regularly as clinical conditions indicate.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityStudies of carcinogenicity, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility have not been conducted with phytonadione.
Pregnancy Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with phytonadione. It is also not known whether phytonadione can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Phytonadione should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing MothersIt is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when phytonadione is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric UseHemolysis, jaundice, and hyperbilirubinemia in newborns, particularly in premature infants, may be related to the dose of phytonadione. Therefore, the recommended dose should not be exceeded (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactoid reactions and deaths have been reported following parenteral administration. The majority of these reported events occurred following intravenous administration (see Box Warning.)
The possibility of allergic sensitivity, including an anaphylactoid reaction, should be kept in mind following parenteral administration.
Transient “flushing sensations” and “peculiar” sensations of taste have been observed, as well as rare instances of dizziness, rapid and weak pulse, profuse sweating, brief hypotension, dyspnea, and cyanosis.
Pain, swelling, and tenderness at the injection site may occur.
Infrequently, usually after repeated injection, erythematous, indurated, pruritic plaques have occurred; rarely, these have progressed to scleroderma-like lesions that have persisted for long periods. In other cases, these lesions have resembled erythema perstans.
Hyperbilirubinemia has been observed in the newborn following administration of phytonadione. This has occurred rarely and primarily with doses above those recommended. (See PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use.)
OVERDOSAGE
The intravenous LD50 of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP in the mouse is 41.5 and 52 mL/kg for the 0.2% and 1.0% concentrations, respectively.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Whenever possible, phytonadione should be given by the subcutaneous route (see Box WARNING). When intravenous or intramuscular administration is considered unavoidable, the drug should be injected very slowly, not exceeding 1 mg per minute.
Protect from light at all times.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration,whenever solution and container permit.
Directions for Dilution
Phytonadione may be diluted with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, 5% Dextrose Injection, or 5% Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection. Benzyl alcohol as a preservative has been associated with toxicity in newborns. Therefore, all of the above diluents should be preservative-free. (See WARNINGS) Other diluents should not be used. When dilutions are indicated, administration should be started immediately after mixture with the diluent, and unused portions of the dilution should be discarded, as well as unused contents of the vial.
Prophylaxis of Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that vitamin K1 be given to the newborn. A single intramuscular dose of phytonadione 0.5 to 1 mg within one hour of birth is recommended.
Treatment of Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
Empiric administration of vitamin K1 should not replace proper laboratory evaluation of the coagulation mechanism. A prompt response (shortening of the prothrombin time in 2 to 4 hours) following administration of vitamin K1 is usually diagnostic of hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, and failure to respond indicates another diagnosis or coagulation disorder.
Phytonadione 1 mg should be given either subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Higher doses may be necessary if the mother has been receiving oral anticoagulants.
Whole blood or component therapy may be indicated if bleeding is excessive. This therapy, however, does not correct the underlying disorder and phytonadione should be given concurrently.
Anticoagulant-lnduced Prothrombin Deficiency in Adults
To correct excessively prolonged prothrombin time caused by oral anticoagulant therapy 2.5 to 10 mg or up to 25 mg initially is recommended. In rare instances 50 mg may be required. Frequency and amount of subsequent doses should be determined by prothrombin time response or clinical condition (see WARNINGS). If in 6 to 8 hours after parenteral administration the prothrombin time has not been shortened satisfactorily, the dose should
berepeated.
Phytonadione Summary of Dosage Guidelines (See insert text for details)
| Newborns |
Dosage |
|
Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
Prophylaxis
Treatment |
0.5 - 1 mg IM within 1 hour of birth
1 mg SC or IM
(Higher doses may be necessary if
the mother has been receiving
oral anti-coagulants) |
| Adults |
Initial Dosage |
|
Anticoagulant - Induced
Prothrombin Deficiency
(caused by coumarin or
indanedione derivatives) |
2.5 mg - 10 mg or
up to 25 mg
(rarely 50 mg) |
|
Hypoprothrombinemia due to
other causes
(Antibiotics; Salicylates or other drugs;
Factors limiting absorption or synthesis) |
2.5 mg - 25 mg or
more (rarely up to 50 mg) | In the event of shock or excessive blood loss, the use of whole blood or component therapy is indicated.
Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Other Causes in Adults
A dosage of 2.5 to 25 mg or more (rarely up to 50 mg) is recommended, the amount and route of administration depending upon the severity of the condition and response obtained.
If possible, discontinuation or reduction of the dosage of drugs interfering with coagulation mechanisms (such as salicylates, antibiotics) is suggested as an alternative to administering concurrent phytonadione. The severity of the coagulation disorder should determine whether the immediate administration of phytonadione is required in addition to discontinuation or reduction of interfering drugs.
HOW SUPPLIED
In unit use packages containing one single dose vial and a SAF-T-Jet® vial injector, 27 G. x 1/2” needle.
Phytonadione Injection USP, 1 mg in 0.5 mL
Stock No. 1240 NDC 76329-1240-1
10 individual cartons shrink wrapped as a group of 10 cartons.
Syringe Assembly Directions:
See User Guide
USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not remove from carton or assemble until ready to use.

*CAUTION: IMPROPER ENGAGING MAY CAUSE GLASS BREAKAGE AND SUBSEQUENT INJURY.
Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP].
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP - User Guide
IMS Saf-T-Jet® Safety Needle
USER GUIDE
NOTE: USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not assemble until ready to use
1 Ensure shield is in the UP position (see inset), then remove protective caps from vial and injector.
2 Align vial such that the injector needle is centered on the stopper. Thread vial into injection 3 half turns to ensure the needle penetrates stopper. Do not push the injector needle into stopper.
3
a) Flip shield down.
b) Remove needle cover PULLING STRAIGHT UP (DO NOT TWIST). Expel air.
4 Administer injection following the established aseptic technique.
5 Position shield in preparation for device activation: Using a one-handed technique, push the tab forward with your finger or thumb so that the shield is less than 90 degrees from the needle. NOTE: Keep your finger or thumb behind the tab at all times.
6 Activate shield: Position the shield approximately 45 degrees to flat surface. Press down with a GENTLE, QUICK MOTION until a distinct AUDIBLE CLICK is heard. Note: Audible click may not be heard on small needle sizes: visual confirmation is required.
7VISUALLY CONFIRM that needle is fully engaged under lock.
8 Following activation of the needle shield, immediately discard the unit into an approved sharps container.
完成资料附件:https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e0b0c8f1-75be-4f25-898a-7b97b608c615
---------------------------------------------------
产地国家: 美国
原产地英文商品名:
PHYTONADIONE 1MG/0.5ML/SYRINGE 25SYRINGES/BOX
原产地英文药品名:
Phytonadione
中文参考商品译名:
维生素K1 1毫克/0.5毫升/注射器 25注射器/盒
中文参考药品译名:
维生素K1
生产厂家中文参考译名:
INTL MEDICATION
生产厂家英文名:
INTL MEDICATION
|




