|
英文药名: Mepron(Atovaquone Oral Suspension) 中文药名: 阿托喹酮口服混悬液 生产厂家: 葛兰素史克公司
Rash occurred more often in subjects treated with MEPRON suspension (46%) than in subjects treated with aerosolized pentamidine (28%). Treatment‑limiting adverse reactions occurred in 25% of subjects treated with MEPRON suspension 1,500 mg once daily and in 7% of subjects treated with aerosolized pentamidine. The most frequent adverse reactions requiring discontinuation of dosing in the group receiving MEPRON suspension 1,500 mg once daily were rash (6%), diarrhea (4%), and nausea (3%). The most frequent adverse reaction requiring discontinuation of dosing in the group receiving aerosolized pentamidine was bronchospasm (2%). Table 2. Percentage (≥20%) of Subjects with Selected Adverse Reactions in the Aerosolized Pentamidine Comparative PCP Prevention Trial
PCP Treatment Trials Safety information is presented from 2 clinical efficacy trials of the MEPRON tablet formulation: 1) a randomized, double‑blind trial comparing MEPRON tablets with TMP‑SMX in subjects with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and mild‑to‑moderate PCP [(A‑a)DO2] ≤45 mm Hg and PaO2 ≥60 mm Hg on room air; 2) a randomized, open-label trial comparing MEPRON tablets with intravenous (IV) pentamidine isethionate in subjects with mild‑to‑moderate PCP who could not tolerate trimethoprim or sulfa antimicrobials. TMP‑SMX Comparative Trial: In the TMP‑SMX comparative trial (n = 408), the majority of subjects were white (66%) and male (95%); the mean age was 36 years. Subjects received MEPRON 750 mg (three 250‑mg tablets) 3 times daily for 21 days or TMP 320 mg plus SMX 1,600 mg 3 times daily for 21 days; median durations of exposure were 21 and 15 days, respectively. Table 3 summarizes all clinical adverse reactions reported by ≥10% of the trial population regardless of attribution. Nine percent of subjects who received MEPRON and 24% of subjects who received TMP‑SMX discontinued therapy due to an adverse reaction. Among the subjects who discontinued, 4% of subjects receiving MEPRON and 8% of subjects in the TMP-SMX group discontinued therapy due to rash. The incidence of adverse reactions with MEPRON suspension at the recommended dose (750 mg twice daily) was similar to that seen with the tablet formulation. Table 3. Percentage (≥10%) of Subjects with Selected Adverse Reactions in the TMP-SMX Comparative PCP Treatment Trial
Pentamidine Comparative Trial: In the pentamidine comparative trial (n = 174), the majority of subjects in the primary therapy trial population (n = 145) were white (72%) and male (97%); the mean age was 37 years. Subjects received MEPRON 750 mg (three 250‑mg tablets) 3 times daily for 21 days or a 3- to 4‑mg/kg single pentamidine isethionate IV infusion daily for 21 days; the median durations of exposure were 21 and 14 days, respectively. Table 4 summarizes the clinical adverse reactions reported by ≥10% of the primary therapy trial population regardless of attribution. Fewer subjects who received MEPRON reported adverse reactions than subjects who received pentamidine (63% vs. 72%). However, only 7% of subjects discontinued treatment with MEPRON due to adverse reactions, while 41% of subjects who received pentamidine discontinued treatment for this reason. Of the 5 subjects who discontinued therapy with MEPRON, 3 reported rash (4%). Rash was not severe in any subject. The most frequently cited reasons for discontinuation of pentamidine therapy were hypoglycemia (11%) and vomiting (9%). Table 4. Percentage (≥10%) of Subjects with Selected Adverse Reactions in the Pentamidine Comparative PCP Treatment Trial (Primary Therapy Group)
6.2 Postmarketing Experience The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of MEPRON suspension. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Methemoglobinemia, thrombocytopenia. Immune System Disorders Hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema, bronchospasm, throat tightness, and urticaria. Eye Disorders Vortex keratopathy. Gastrointestinal Disorders Pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Disorders Hepatitis, fatal liver failure. Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and skin desquamation. Renal and Urinary Disorders Acute renal impairment. 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS 7.1 Rifampin/Rifabutin Concomitant administration of rifampin or rifabutin and MEPRON suspension is known to reduce atovaquone concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant administration of MEPRON suspension and rifampin or rifabutin is not recommended. 7.2 Tetracycline Concomitant administration of tetracycline and MEPRON suspension has been associated with a reduction in plasma concentrations of atovaquone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Caution should be used when prescribing tetracycline concomitantly with MEPRON suspension. Monitor patients for potential loss of efficacy of MEPRON if coadministration is necessary. 7.3 Metoclopramide Metoclopramide may reduce the bioavailability of atovaquone and should be used only if other antiemetics are not available [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 7.4 Indinavir Concomitant administration of atovaquone and indinavir did not result in any change in the steady-state AUC and Cmax of indinavir but resulted in a decrease in the Ctrough of indinavir [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Caution should be exercised when prescribing MEPRON suspension with indinavir due to the decrease in trough concentrations of indinavir. Monitor patients for potential loss of efficacy of indinavir if coadministration with MEPRON suspension is necessary. 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy Pregnancy Category C There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. MEPRON should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Atovaquone was not teratogenic and did not cause reproductive toxicity in rats at plasma concentrations up to 2 to 3 times the estimated human exposure (dose of 1,000 mg/kg/day in rats). Atovaquone caused maternal toxicity in rabbits at plasma concentrations that were approximately one-half the estimated human exposure. Mean fetal body lengths and weights were decreased and there were higher numbers of early resorption and post‑implantation loss per dam (dose of 1,200 mg/kg/day in rabbits). It is not clear whether these effects were caused by atovaquone directly or were secondary to maternal toxicity. Concentrations of atovaquone in rabbit fetuses averaged 30% of the concurrent maternal plasma concentrations. In a separate study in rats given a single 14C‑radiolabelled dose (1,000 mg/kg), concentrations of radiocarbon in rat fetuses were 18% (middle gestation) and 60% (late gestation) of concurrent maternal plasma concentrations. 8.3 Nursing Mothers It is not known whether atovaquone is excreted into human milk. Because many drugs are excreted into human milk, caution should be exercised when MEPRON is administered to a nursing woman. In a rat study (with doses of 10 and 250 mg/kg), atovaquone concentrations in the milk were 30% of the concurrent atovaquone concentrations in the maternal plasma at both doses. 8.4 Pediatric Use Evidence of safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients (aged 12 years and younger) has not been established. In a trial of MEPRON suspension administered once daily with food for 12 days to 27 HIV-1-infected, asymptomatic infants and children aged between 1 month and 13 years, the pharmacokinetics of atovaquone were age-dependent. The average steady-state plasma atovaquone concentrations in the 24 subjects with available concentration data are shown in Table 5. Table 5. Average Steady-state Plasma Atovaquone Concentrations in Pediatric Subjects
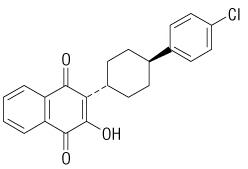
8.5 Geriatric Use Clinical trials of MEPRON did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. 10 OVERDOSAGE In one patient who took an unspecified dose of dapsone, methemoglobinemia occurred. Rash has also been reported after overdose. There is no known antidote for atovaquone, and it is currently unknown if atovaquone is dialyzable. 11 DESCRIPTION MEPRON (atovaquone) is a quinone antimicrobial drug for oral administration. The chemical name of atovaquone is trans-2-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexyl]-3-hydroxy-1,4‑naphthalenedione. Atovaquone is a yellow crystalline solid that is practically insoluble in water. It has a molecular weight of 366.84 and the molecular formula C22H19ClO3. The compound has the following structural formula:
bBased on logistic regression analysis. A dosing regimen of MEPRON suspension for the treatment of mild‑to‑moderate PCP was selected to achieve average plasma atovaquone concentrations of approximately 20 mcg/mL, because this plasma concentration was previously shown to be well tolerated and associated with the highest treatment success rates (Table 6). In an open‑label PCP treatment trial with MEPRON suspension, dosing regimens of 1,000 mg once daily, 750 mg twice daily, 1,500 mg once daily, and 1,000 mg twice daily were explored. The average steady‑state plasma atovaquone concentration achieved at the 750‑mg twice‑daily dose given with meals was 22.0 ± 10.1 mcg/mL (n = 18). Drug Interactions Rifampin/Rifabutin: In a trial with 13 HIV-1-infected volunteers, the oral administration of rifampin 600 mg every 24 hours with MEPRON suspension 750 mg every 12 hours resulted in a 52% ± 13% decrease in the average steady‑state plasma atovaquone concentration and a 37% ± 42% increase in the average steady‑state plasma rifampin concentration. The half‑life of atovaquone decreased from 82 ± 36 hours when administered without rifampin to 50 ± 16 hours with rifampin. In a trial of 24 healthy volunteers, the oral administration of rifabutin 300 mg once daily with MEPRON suspension 750 mg twice daily resulted in a 34% decrease in the average steady‑state plasma atovaquone concentration and a 19% decrease in the average steady‑state plasma rifabutin concentration. Tetracycline: Concomitant treatment with tetracycline has been associated with a 40% reduction in plasma concentrations of atovaquone. Metoclopramide: Concomitant treatment with metoclopramide has been associated with decreased bioavailability of atovaquone. Indinavir: Concomitant administration of atovaquone (750 mg twice daily with food for 14 days) and indinavir (800 mg three times daily without food for 14 days) did not result in any change in the steady‑state AUC and Cmax of indinavir, but resulted in a decrease in the Ctrough of indinavir (23% decrease [90% CI: 8%, 35%]). Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole: The possible interaction between atovaquone and TMP‑SMX was evaluated in 6 HIV-1-infected adult volunteers as part of a larger multiple‑dose, dose‑escalation, and chronic dosing trial of MEPRON suspension. In this crossover trial, MEPRON suspension 500 mg once daily (not the approved dosage), or TMP‑SMX tablets (trimethoprim 160 mg and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg) twice daily, or the combination were administered with food to achieve steady state. No difference was observed in the average steady‑state plasma atovaquone concentration after coadministration with TMP‑SMX. Coadministration of MEPRON with TMP‑SMX resulted in a 17% and 8% decrease in average steady‑state concentrations of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in plasma, respectively. Zidovudine: Data from 14 HIV-1-infected volunteers who were given atovaquone tablets 750 mg every 12 hours with zidovudine 200 mg every 8 hours showed a 24% ± 12% decrease in zidovudine apparent oral clearance, leading to a 35% ± 23% increase in plasma zidovudine AUC. The glucuronide metabolite:parent ratio decreased from a mean of 4.5 when zidovudine was administered alone to 3.1 when zidovudine was administered with atovaquone tablets. This effect is minor and would not be expected to produce clinically significant events. Zidovudine had no effect on atovaquone pharmacokinetics. 12.4 Microbiology Mechanism of Action Atovaquone is a hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, an analog of ubiquinone, with antipneumocystis activity. The mechanism of action against Pneumocystis jiroveci has not been fully elucidated. In Plasmodium species, the site of action appears to be the cytochrome bc1 complex (Complex III). Several metabolic enzymes are linked to the mitochondrial electron transport chain via ubiquinone. Inhibition of electron transport by atovaquone results in indirect inhibition of these enzymes. The ultimate metabolic effects of such blockade may include inhibition of nucleic acid and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis. Activity In Vitro Several laboratories, using different in vitro methodologies, have shown the IC50 (50% inhibitory concentration) of atovaquone against P. jiroveci to be 0.1 to 3.0 mcg/mL. Drug Resistance Phenotypic resistance to atovaquone in vitro has not been demonstrated for P. jiroveci. However, in 2 subjects who developed PCP after prophylaxis with atovaquone, DNA sequence analysis identified mutations in the predicted amino acid sequence of P. jiroveci cytochrome b (a likely target site for atovaquone). The clinical significance of this is unknown. 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Carcinogenicity studies in rats were negative; 24‑month studies in mice (dosed with 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg/day), showed treatment‑related increases in incidence of hepatocellular adenoma and hepatocellular carcinoma at all doses tested, which correlated with 1.4 to 3.6 times the average steady‑state plasma concentrations in humans during acute treatment of PCP. Atovaquone was negative with or without metabolic activation in the Ames Salmonella mutagenicity assay, the mouse lymphoma mutagenesis assay, and the cultured human lymphocyte cytogenetic assay. No evidence of genotoxicity was observed in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. 14 CLINICAL STUDIES 14.1 Prevention of PCP The indication for prevention of PCP is based on the results of 2 clinical trials comparing MEPRON suspension with dapsone or aerosolized pentamidine in HIV-1-infected adolescent (aged 13 to 18 years) and adult subjects at risk of PCP (CD4 count <200 cells/mm3 or a prior episode of PCP) and unable to tolerate TMP‑SMX. Dapsone Comparative Trial This open-label trial enrolled 1,057 subjects, randomized to receive MEPRON suspension 1,500 mg once daily (n = 536) or dapsone 100 mg once daily (n = 521). The majority of subjects were white (64%), male (88%), and receiving prophylaxis for PCP at randomization (73%); the mean age was 38 years. Median follow-up was 24 months. Subjects randomized to the dapsone arm who were seropositive for Toxoplasma gondii and had a CD4 count <100 cells/mm3 also received pyrimethamine and folinic acid. PCP event rates are shown in Table 7. Mortality rates were similar. Aerosolized Pentamidine Comparative Trial This open‑label trial enrolled 549 subjects, randomized to receive MEPRON suspension 1,500 mg once daily (n = 175), MEPRON suspension 750 mg once daily (n = 188), or aerosolized pentamidine 300 mg once monthly (n = 186). The majority of subjects were white (79%), male (92%), and were primary prophylaxis patients at enrollment (58%); the mean age was 38 years. Median follow-up was 11.3 months. The results of the PCP event rates appear in Table 7. Mortality rates were similar among the groups. Table 7. Confirmed or Presumed/Probable PCP Events (As-Treated Analysis)a
bRelative risk <1 favors MEPRON and values >1 favor comparator. Trial results did not show superiority of MEPRON to the comparator. cThe confidence level of the interval for the dapsone comparative trial was 95% and for the pentamidine comparative trial was 97.5%. An analysis of all PCP events (intent-to-treat analysis) for both trials showed results similar to those shown in Table 7. 14.2 Treatment of PCP The indication for treatment of mild‑to‑moderate PCP is based on the results of two efficacy trials: a randomized, double‑blind trial comparing MEPRON tablets with TMP‑SMX in subjects with HIV/AIDS and mild‑to‑moderate PCP (defined in the protocol as [(A‑a)DO2] ≤45 mm Hg and PaO2 ≥60 mm Hg on room air) and a randomized open-label trial comparing MEPRON tablets with IV pentamidine isethionate in subjects with mild‑to‑moderate PCP who could not tolerate trimethoprim or sulfa antimicrobials. Both trials were conducted with the tablet formulation using 750 mg three times daily. Results from these efficacy trials established a relationship between plasma atovaquone concentration and successful outcome. Successful outcome was defined as improvement in clinical and respiratory measures persisting at least 4 weeks after cessation of therapy. Comparative pharmacokinetic trials of the suspension and tablet formulations established the currently recommended suspension dose of 750 mg twice daily [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. TMP‑SMX Comparative Trial This double‑blind, randomized trial compared the safety and efficacy of MEPRON tablets with that of TMP‑SMX for the treatment of subjects with HIV/AIDS and histologically confirmed PCP. Only subjects with mild‑to‑moderate PCP were eligible for enrollment. A total of 408 subjects were enrolled into the trial. The majority of subjects were white (66%) and male (95%); the mean age was 36 years. Eighty‑six subjects without histologic confirmation of PCP were excluded from the efficacy analyses. Of the 322 subjects with histologically confirmed PCP, 160 were randomized to receive 750 mg MEPRON (three 250-mg tablets) 3 times daily for 21 days and 162 were randomized to receive 320 mg TMP plus 1,600 mg SMX 3 times daily for 21 days. Therapy success was defined as improvement in clinical and respiratory measures persisting at least 4 weeks after cessation of therapy. Improvement in clinical and respiratory measures was assessed using a composite of parameters that included oral body temperature, respiratory rate, severity scores for cough, dyspnea, and chest pain/tightness. Therapy failures included lack of response, treatment discontinuation due to an adverse experience, and unevaluable. There was a significant difference (P = 0.03) in mortality rates between the treatment groups favoring TMP-SMX. Among the 322 subjects with confirmed PCP, 13 of 160 (8%) subjects treated with MEPRON and 4 of 162 (2.5%) subjects receiving TMP‑SMX died during the 21‑day treatment course or 8‑week follow‑up period. In the intent‑to‑treat analysis for all 408 randomized subjects, there were 16 (8%) deaths among subjects treated with MEPRON and 7 (3.4%) deaths among subjects treated with TMP‑SMX (P = 0.051). Of the 13 subjects with confirmed PCP and treated with MEPRON who died, 4 died of PCP and 5 died with a combination of bacterial infections and PCP; bacterial infections did not appear to be a factor in any of the 4 deaths among TMP‑SMX‑treated subjects. A correlation between plasma atovaquone concentrations and death demonstrated that subjects with lower plasma concentrations were more likely to die. For those subjects for whom Day 4 plasma atovaquone concentration data are available, 5 (63%) of 8 subjects with concentrations <5 mcg/mL died during participation in the trial. However, only 1 (2.0%) of the 49 subjects with Day 4 plasma atovaquone concentrations ≥5 mcg/mL died. Sixty-two percent of subjects on MEPRON and 64% of subjects on TMP‑SMX were classified as protocol-defined therapy successes (Table 8). Table 8. Outcome of Treatment for PCP-positive Subjects Enrolled in the TMP-SMX Comparative Trial
The failure rate due to lack of response was significantly higher for subjects receiving MEPRON, while the failure rate due to an adverse reaction was significantly higher for subjects receiving TMP‑SMX. Pentamidine Comparative Trial This unblinded, randomized trial was designed to compare the safety and efficacy of MEPRON with that of pentamidine for the treatment of histologically confirmed mild or moderate PCP in subjects with HIV/AIDS. Approximately 80% of the subjects either had a history of intolerance to trimethoprim or sulfa antimicrobials (the primary therapy group) or were experiencing intolerance to TMP‑SMX with treatment of an episode of PCP at the time of enrollment in the trial (the salvage treatment group). A total of 174 subjects were enrolled into the trial. Subjects were randomized to receive MEPRON 750 mg (three 250‑mg tablets) 3 times daily for 21 days or pentamidine isethionate 3- to 4‑mg/kg single IV infusion daily for 21 days. The majority of subjects were white (72%) and male (97%); the mean age was approximately 37 years. Thirty‑nine subjects without histologic confirmation of PCP were excluded from the efficacy analyses. Of the 135 subjects with histologically confirmed PCP, 70 were randomized to receive MEPRON and 65 to pentamidine. One hundred and ten (110) of these were in the primary therapy group and 25 were in the salvage therapy group. One subject in the primary therapy group randomized to receive pentamidine did not receive trial medication. There was no difference in mortality rates between the treatment groups. Among the 135 subjects with confirmed PCP, 10 of 70 (14%) subjects receiving MEPRON and 9 of 65 (14%) subjects receiving pentamidine died during the 21‑day treatment course or 8‑week follow‑up period. In the intent‑to‑treat analysis for all subjects, there were 11 (12.5%) deaths among those treated with MEPRON and 12 (14%) deaths among those treated with pentamidine. Among subjects for whom Day 4 plasma atovaquone concentrations were available, 3 of 5 (60%) subjects with concentrations <5 mcg/mL died during participation in the trial. However, only 2 of 21 (9%) subjects with Day 4 plasma concentrations ≥5 mcg/mL died. The therapeutic outcomes for the 134 subjects who received trial medication in this trial are presented in Table 9. Table 9. Outcome of Treatment for PCP-positive Subjects (%) Enrolled in the Pentamidine Comparative Trial
MEPRON suspension (bright yellow, citrus-flavored) containing 750 mg atovaquone in 5 mL. • Bottle of 210 mL with child-resistant cap (NDC 0173-0665-18). Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F). Do not freeze. Dispense in tight container as defined in USP. • 5‑mL child‑resistant foil pouch ‑ unit dose pack of 42 (NDC 0173-0547-00). Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F). Do not freeze. 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION Administration Instructions Instruct patients to: • Ensure the prescribed dose of MEPRON suspension is taken as directed. • Take their daily doses of MEPRON suspension with food, as food will significantly improve the absorption of the drug. • Shake MEPRON suspension gently before use each time. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=b426b6bf-f07e-4580-97ae-dfca1ddf5b8f | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||